Genetic counseling and testing for females at elevated risk for breast cancer: Protocol for the randomized controlled trial of the Know Your Risk intervention
- PMID: 37661005
- PMCID: PMC10591709
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cct.2023.107323
Genetic counseling and testing for females at elevated risk for breast cancer: Protocol for the randomized controlled trial of the Know Your Risk intervention
Abstract
Background: Genetic counseling and testing have an important role in the care of patients at elevated risk for breast cancer. However, conventional pre- and post-test genetic counseling is labor and time intensive, less accessible for patients living outside major urban centers, and impractical on a large scale. A patient-driven approach to genetic counseling and testing may increase access, improve patients' experiences, affect efficiency of clinical practice, and help meet workforce demand. The objective of this 2-arm randomized controlled trial is to determine the efficacy of Know Your Risk (KYR), a genetic counseling patient preference intervention.
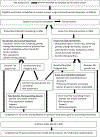
Methods: Females (n = 1000) at elevated risk (>20% lifetime) for breast cancer will be randomized to the KYR intervention or conventional genetic counseling. The study will provide comprehensive assessment of breast cancer risk by multigene panel testing and validated polygenic risk score. Primary outcome is adherence to National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines for a clinical encounter every 6-12 months and an annual mammogram (breast MRI if recommended) determined by medical record review. Secondary outcomes include adherence to other recommended cancer screening tests determined by medical record review and changes in breast cancer knowledge, perception of risk, post-test/counseling distress, and satisfaction with counseling by completion of three surveys during the study. Study aims will be evaluated for non-inferiority of the KYR intervention compared to conventional genetic counseling.
Conclusion: If efficacious, the KYR intervention has the potential to improve patients' experience and may change how genetic counseling is delivered, inform best practices, and reduce workforce burden.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.govNCT05325151.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Genetic counseling; Genetic testing; Patient education; Polygenic; Randomized controlled trial.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Egan KM, Stampfer MJ, Rosner BA, Trichopoulos D, Newcomb PA, Trentham-Dietz A, Longnecker MP, Mittendorf R, Greenberg ER, Willett WC, Risk factors for breast cancer in women with a breast cancer family history, Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 7(5) (1998) 359–64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical