Anti-parasitic drug discovery against Babesia microti by natural compounds: an extensive computational drug design approach
- PMID: 37662005
- PMCID: PMC10469490
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1222913
Anti-parasitic drug discovery against Babesia microti by natural compounds: an extensive computational drug design approach
Abstract
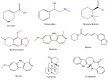
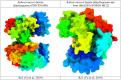
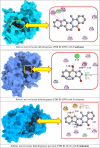
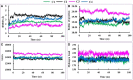
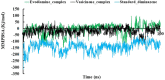
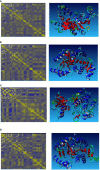
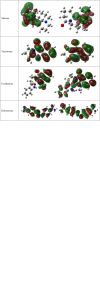
Tick-borne Babesiosis is a parasitic infection caused by Babesia microti that can infect both animals and humans and may spread by tick, blood transfusions, and organ transplantation. The current therapeutic options for B. microti are limited, and drug resistance is a concern. This study proposes using computational drug design approaches to find and design an effective drug against B. microti. The study investigated the potentiality of nine natural compounds against the pathogenic human B. microti parasite and identified Vasicinone and Evodiamine as the most promising drugs. The ligand structures were optimized using density functional theory, molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulations, quantum mechanics such as HOMO-LUMO, drug-likeness and theoretical absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicity (ADMET), and pharmacokinetics characteristics performed. The results showed that Vasicinone (-8.6 kcal/mol and -7.8 kcal/mol) and Evodiamine (-8.7 kcal/mol and -8.5 kcal/mol) had the highest binding energy and anti-parasitic activity against B. microti lactate dehydrogenase and B. microti lactate dehydrogenase apo form. The strongest binding energy was reported by Vasicinone and Evodiamine; the compounds were evaluated through molecular dynamics simulation at 100 ns, and their stability when they form complexes with the targeted receptors was determined. Finally, the pkCSM web server is employed to predict the ADMET qualities of specific molecules, which can help prevent negative effects that arise from taking the treatment. The SwissADME web server is used to assess the Lipinski rule of five and drug-likeness properties including topological polar surface area and bioavailability. The Lipinski rule is used to estimate significant drug-likeness. The theoretical pharmacokinetics analysis and drug-likeness of the selected compounds are confirmed to be accepted by the Lipinski rule and have better ADMET features. Thus, to confirm their experimental value, these mentioned molecules should be suggested to carry out in wet lab, pre-clinical, and clinical levels.
Keywords: ADMET; B. microti; DFT; and drug design; molecular docking; molecular dynamic simulation.
Copyright © 2023 Akash, Hosen, Mahmood, Supti, Kumer, Sultana, Jannat, Bayıl, Nafidi, Jardan, Mekonnen and Bourhia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abraham A., Thekkiniath J., Kilian N., Lawres L., Gao R., Debus K., et al. (2018). Establishment of a continuous In vitro culture of babesia duncani in human erythrocytes reveals unusually high tolerance to recommended therapies. J. Of. Biol. Chem. 293, 19974–19981. doi: 10.1074/jbc.AC118.005771 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aguero-Rosenfeld M. (2011). “Committee on Lyme disease and other tick-borne diseases: the state of the science, institute of medicine,” in Critical needs and gaps in understanding prevention, amelioration, and resolution of Lyme and other tick-borne diseases [Electronic resource]: the short-term and long-term outcomes: workshop report [Internet] (Washington, DC: National Academies Press; ). - PubMed
-
- Babes V. (1888). Sur l’hemoglobinurie bacterienne Du boeuf. Cr. Acad. Sci. 107, 692–694.
-
- Baildya N., Khan A. A., Ghosh N. N., Dutta T., Chattopadhyay A. P. (2021). Screening of potential drug from azadirachta indica (Neem) extracts for SARS-Cov-2: an insight from molecular docking and MD-simulation studies. J. Of. Mol. Structure. 1227, 129390. doi: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2020.129390 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bastos R. G., Thekkiniath J., Ben Mamoun C., Fuller L., Molestina R. E., Florin-Christensen M., et al. (2021). Babesia microti immunoreactive rhoptry-associated protein-1 paralogs are ancestral members of the piroplasmid-confined rap-1 family. Pathogens 10, 1384. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10111384 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

