Whole genome sequence and diversity in multigene families of Babesia ovis
- PMID: 37662008
- PMCID: PMC10471129
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1194608
Whole genome sequence and diversity in multigene families of Babesia ovis
Abstract
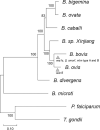
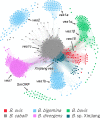
Ovine babesiosis, caused by Babesia ovis, is an acute, lethal, and endemic disease worldwide and causes a huge economic loss to animal industry. Pathogen genome sequences can be utilized for selecting diagnostic markers, drug targets, and antigens for vaccine development; however, those for B. ovis have not been available so far. In this study, we obtained a draft genome sequence for B. ovis isolated from an infected sheep in Turkey. The genome size was 7.81 Mbp with 3,419 protein-coding genes. It consisted of 41 contigs, and the N50 was 526 Kbp. There were 259 orthologs identified among eight Babesia spp., Plasmodium falciparum, and Toxoplasma gondii. A phylogeny was estimated on the basis of the orthologs, which showed B. ovis to be closest to B. bovis. There were 43 ves genes identified using hmm model as well. They formed a discriminating cluster to other ves multigene family of Babesia spp. but showed certain similarities to those of B. bovis, B. caballi, and Babesia sp. Xinjiang, which is consistent with the phylogeny. Comparative genomics among B. ovis and B. bovis elucidated uniquely evolved genes in these species, which may account for the adaptation.
Keywords: Babesia ovis; apicomplexa; comparative genomics; multigene families; ovine babesiosis.
Copyright © 2023 Yamagishi, Ceylan, Xuan and Sevinc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Altenhoff A. M., Škunca N., Glover N., Train C.-M., Sueki A., Piližota I., et al. . (2015). The OMA orthology database in 2015: function predictions, better plant support, synteny view and other improvements. Nucleic Acids Res. 43 (Database issue), D240–D249. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1158 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

