Eco-friendly synthesized nanoparticles as antimicrobial agents: an updated review
- PMID: 37662011
- PMCID: PMC10472938
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1224778
Eco-friendly synthesized nanoparticles as antimicrobial agents: an updated review
Abstract
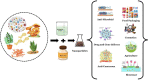
Green synthesis of NPs has gained extensive acceptance as they are reliable, eco-friendly, sustainable, and stable. Chemically synthesized NPs cause lung inflammation, heart problems, liver dysfunction, immune suppression, organ accumulation, and altered metabolism, leading to organ-specific toxicity. NPs synthesized from plants and microbes are biologically safe and cost-effective. These microbes and plant sources can consume and accumulate inorganic metal ions from their adjacent niches, thus synthesizing extracellular and intracellular NPs. These inherent characteristics of biological cells to process and modify inorganic metal ions into NPs have helped explore an area of biochemical analysis. Biological entities or their extracts used in NPs include algae, bacteria, fungi, actinomycetes, viruses, yeasts, and plants, with varying capabilities through the bioreduction of metallic NPs. These biosynthesized NPs have a wide range of pharmaceutical applications, such as tissue engineering, detection of pathogens or proteins, antimicrobial agents, anticancer mediators, vehicles for drug delivery, formulations for functional foods, and identification of pathogens, which can contribute to translational research in medical applications. NPs have various applications in the food and drug packaging industry, agriculture, and environmental remediation.
Keywords: DNA damage; anticancer agents; antimicrobial agents; antioxidant activity; drug delivery; eco-friendly; green synthesis.
Copyright © 2023 Borehalli Mayegowda, Roy, N. G., Pandit, Alghamdi, Almehmadi, Allahyani, Awwad and Sharma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



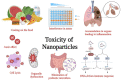
References
-
- Adarsha J. R., Ravishankar T. N., Ananda A., Manjunatha C. R., Shilpa B. M., Ramakrishnappa T. (2022). Hydrothermal synthesis of novel heterostructured Ag/TiO 2 /CuFe 2 O 4 nanocomposite: Characterization, enhanced photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye, and efficient antibacterial studies. Water Environ. Res. 94 (6), e10744. doi: 10.1002/wer.10744 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aguilar-Méndez M. A., Martín-Martínez E. S., Ortega-Arroyo L., Coblan-Portillo G., Sanchez-Espindola E. (2010). Synthesis and Characterization of silver nanoparticles: effect on phytopathogen Colletotrichum gloesporoides. J. Nanoparticle Re-search; 152, 404–416. doi: 10.1007/s11051-010-0145-6 - DOI
-
- Ananda A., Ramakrishnappa T., Archana S., Reddy Yadav L. S., Shilpa B. M., Nagaraju G., et al. . (2022). Green synthesis of MgO nanoparticles using Phyllanthus emblica for Evans blue degradation and antibacterial activity. Materials Today: Proc. 49, 801–810. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2021.05.340 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

