This is a preprint.
Reprogramming of breast tumor-associated macrophages with modulation of arginine metabolism
- PMID: 37662241
- PMCID: PMC10473631
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.08.22.554238
Reprogramming of breast tumor-associated macrophages with modulation of arginine metabolism
Update in
-
Reprogramming of breast tumor-associated macrophages with modulation of arginine metabolism.Life Sci Alliance. 2024 Aug 27;7(11):e202302339. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202302339. Print 2024 Nov. Life Sci Alliance. 2024. PMID: 39191486 Free PMC article.
Abstract
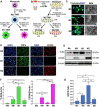
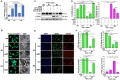
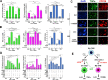
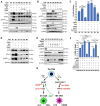
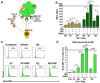
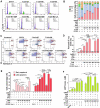
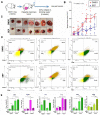
HER2+ breast tumors have abundant immune-suppressive cells, including M2-type tumor associated macrophages (TAMs). While TAMs consist of the immune-stimulatory M1-type and immune-suppressive M2-type, M1/M2-TAM ratio is reduced in immune-suppressive tumors, contributing to their immunotherapy refractoriness. M1 vs. M2-TAM formation depends on differential arginine metabolism, where M1-TAMs convert arginine to nitric oxide (NO) and M2-TAMs convert arginine to polyamines (PAs). We hypothesize that such distinct arginine metabolism in M1- vs M2-TAMs is attributed to different availability of BH4 (NO synthase cofactor) and that its replenishment would reprogram M2-TAMs to M1-TAMs. Recently, we reported that sepiapterin (SEP), the endogenous BH4 precursor, elevates the expression of M1-TAM markers within HER2+ tumors. Here, we show that SEP restores BH4 levels in M2-TAMs, which then redirects arginine metabolism to NO synthesis and converts M2-TAMs to M1-TAMs. The reprogrammed TAMs exhibit full-fledged capabilities of antigen presentation and induction of effector T cells to trigger immunogenic cell death of HER2+ cancer cells. This study substantiates the utility of SEP in metabolic shift of HER2+ breast tumor microenvironment as a novel immunotherapeutic strategy.
Keywords: HER2; breast cancer; nitric oxide; polyamines; tetrahydrobiopterin.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure and competing interests statement The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Antoniades C., Cunnington C., Antonopoulos A., Neville M., Margaritis M., Demosthenous M., Bendall J., Hale A., Cerrato R., Tousoulis D., Bakogiannis C., Marinou K., Toutouza M., Vlachopoulos C., Leeson P., Stefanadis C., Karpe F. and Channon K.M. (2011) Induction of Vascular GTP-Cyclohydrolase I and Endogenous Tetrahydrobiopterin Synthesis Protect Against Inflammation-Induced Endothelial Dysfunction in Human Atherosclerosis. Circulation, 124, 1860–1870. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bailey J.D., Diotallevi M., Nicol T., McNeill E., Shaw A., Chuaiphichai S., Hale A., Starr A., Nandi M., Stylianou E., McShane H., Davis S., Fischer R., Kessler B.M., McCullagh J., Channon K.M. and Crabtree M.J. (2019) Nitric Oxide Modulates Metabolic Remodeling in Inflammatory Macrophages through TCA Cycle Regulation and Itaconate Accumulation. Cell Rep, 28, 218–230.e217. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bertani F.R., Mozetic P., Fioramonti M., Iuliani M., Ribelli G., Pantano F., Santini D., Tonini G., Trombetta M., Businaro L., Selci S. and Rainer A. (2017) Classification of M1/M2-polarized human macrophages by label-free hyperspectral reflectance confocal microscopy and multivariate analysis. Scientific Reports, 7, 8965. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
