This is a preprint.
Coxsackievirus infection induces direct pancreatic β-cell killing but poor anti-viral CD8+ T-cell responses
- PMID: 37662376
- PMCID: PMC10473604
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.08.19.553954
Coxsackievirus infection induces direct pancreatic β-cell killing but poor anti-viral CD8+ T-cell responses
Update in
-
Coxsackievirus infection induces direct pancreatic β cell killing but poor antiviral CD8+ T cell responses.Sci Adv. 2024 Mar 8;10(10):eadl1122. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adl1122. Epub 2024 Mar 6. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 38446892 Free PMC article.
Abstract
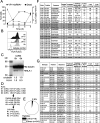
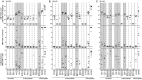
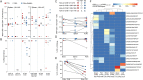
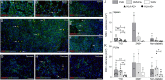
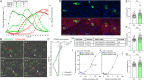
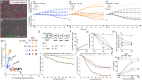
Coxsackievirus B (CVB) infection of pancreatic β cells is associated with β-cell autoimmunity. We investigated how CVB impacts human β cells and anti-CVB T-cell responses. β cells were efficiently infected by CVB in vitro, downregulated HLA Class I and presented few, selected HLA-bound viral peptides. Circulating CD8+ T cells from CVB-seropositive individuals recognized only a fraction of these peptides, and only another sub-fraction was targeted by effector/memory T cells that expressed the exhaustion marker PD-1. T cells recognizing a CVB epitope cross-reacted with the β-cell antigen GAD. Infected β cells, which formed filopodia to propagate infection, were more efficiently killed by CVB than by CVB-reactive T cells. Thus, our in-vitro and ex-vivo data highlight limited T-cell responses to CVB, supporting the rationale for CVB vaccination trials for type 1 diabetes prevention. CD8+ T cells recognizing structural and non-structural CVB epitopes provide biomarkers to differentially follow response to infection and vaccination.
Keywords: Enterovirus; HLA; cytotoxic T lymphocytes; epitopes; glutamic acid decarboxylase; immunopeptidome; mimicry; type 1 diabetes; vaccination.
Conflict of interest statement
H.H. is a board member and stock owner in Vactech Ltd, which develops vaccines against picornaviruses and licensed CVB vaccine-related intellectual property rights to Provention Bio Inc. M.F.-T. serves and A.P. served on the scientific advisory board of Provention Bio Inc. R.M. received research funding from Provention Bio Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Patterson C.C., Harjutsalo V., Rosenbauer J., Neu A., Cinek O., Skrivarhaug T., Rami-Merhar B., Soltesz G., Svensson J., Parslow R.C., et al. (2019). Trends and cyclical variation in the incidence of childhood type 1 diabetes in 26 European centres in the 25 year period 1989–2013: a multicentre prospective registration study. Diabetologia 62, 408–417. 10.1007/s00125-018-4763-3. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Parikka V., Nanto-Salonen K., Saarinen M., Simell T., Ilonen J., Hyoty H., Veijola R., Knip M., and Simell O. (2012). Early seroconversion and rapidly increasing autoantibody concentrations predict prepubertal manifestation of type 1 diabetes in children at genetic risk. Diabetologia 55, 1926–1936. 10.1007/s00125-012-2523-3. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
