Changes and Clinical Value of Serum miR-24 and miR-223 Levels in Patients with Severe Pneumonia
- PMID: 37662504
- PMCID: PMC10473963
- DOI: 10.2147/IJGM.S411966
Changes and Clinical Value of Serum miR-24 and miR-223 Levels in Patients with Severe Pneumonia
Abstract
Introduction: Severe pneumonia progresses rapidly, so early assessment of the severity and prognosis is crucial for reducing mortality rates.
Objective: We explore the role of serum microRNA-24 (miR-24) and microRNA-223 (miR-223) in the prognosis of severe pneumonia.
Methods: There were a total of 96 patients with general pneumonia, 94 patients with severe pneumonia, and 93 healthy people, who were enrolled in this study. The levels of serum miR-24 and miR-223 were detected by real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR in all groups.
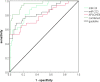
Results: The serum miR-223 level in the severe group was higher than that in the common group and the control group, and the miR-24 level was lower than that in the common group and the control group (P<0.05). The serum miR-223 levels and APACHEII scores in the death group were higher than those in the survival group on the first, third, and seventh day after admission, while the miR-24 levels were lower than those in the survival group (P<0.05). The proportion of patients with mechanical ventilation in the death group was higher than that in the survival group (P<0.05). The level of serum miR-24 was negatively correlated with APACHEII score and mechanical ventilation in patients who died of severe pneumonia (P<0.05), and miR-223 was positively correlated with APACHEII score and mechanical ventilation (P<0.05). The AUC predicted by serum miR-24, miR-223, and APACHEII scores alone and jointly were 0.867, 0.839, 0.791, and 0.952, respectively. MiR-24 and miR-223 are protective and independent risk factors for mortality in severe pneumonia patients, respectively (P<0.05). MiR-24 was a protective factor affecting the death of patients with severe pneumonia, and miR-223 was an independent risk factor affecting the death of patients with severe pneumonia (P<0.05).
Conclusion: The combination of serum miR-24 and miR-223 levels on the first day after admission and APACHEII score can effectively predict prognosis.
Keywords: micro RNA-223; micro RNA-24; prognosis; severe pneumonia.
© 2023 Gao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[The value of serum microRNA-92a and microRNA-146a levels combined with pulmonary ultrasound score in predicting the severity and prognosis of acute respiratory distress syndrome].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020 Oct;32(10):1231-1235. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20200409-00268. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020. PMID: 33198870 Chinese.
-
[Clinical value of serum endocan and procalcitonin in early diagnosis and prognosis evaluation of sepsis].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2017 Apr;29(4):321-326. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2017.04.007. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2017. PMID: 28420465 Chinese.
-
[Value of serum level of microRNA-494 in predicting prognosis of acute renal injury after cardiac surgery in children].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019 Dec;31(12):1469-1473. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2019.12.007. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019. PMID: 32029031 Chinese.
-
[Comparison of simplified acute physiology score III and other scoring systems in prediction of 28-day prognosis in patients with severe sepsis].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2015 Jun;27(6):454-9. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2015.06.008. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2015. PMID: 26049183 Chinese.
-
[The effect of low molecular heparin on the prognosis of severe pneumonia in elderly patients].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2013 Dec;25(12):734-7. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2013.12.009. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2013. PMID: 24447354 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Risk prediction models for mortality in patients with severe pneumonia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jul 23;12:1564545. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1564545. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40771466 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic value of miR-193a-5p in severe pneumonia and its correlation with prognosis.J Cardiothorac Surg. 2025 Jan 23;20(1):87. doi: 10.1186/s13019-024-03256-y. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2025. PMID: 39849492 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stem cells derived exosomes: a new era in cardiac regeneration.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025 Jan 23;16(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s13287-024-04123-2. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 39849585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasma EV-miRNAs as Potential Biomarkers of COVID-19 Vaccine Immune Response in Cancer Patients.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Jul 28;12(8):848. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12080848. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39203974 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eldaboosy S, Almoosa Z, Saad M, et al. Comparison between physiological scores SIPF, CURB-65, and APACHE II as predictors of prognosis and mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 pneumonia: a multicenter study, Saudi Arabia. Infect Drug Resist. 2022;15:7619–7630. doi:10.2147/IDR.S395095 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources