Yeast gene KTI13 (alias DPH8) operates in the initiation step of diphthamide synthesis on elongation factor 2
- PMID: 37662670
- PMCID: PMC10468694
- DOI: 10.15698/mic2023.09.804
Yeast gene KTI13 (alias DPH8) operates in the initiation step of diphthamide synthesis on elongation factor 2
Abstract
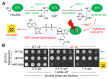
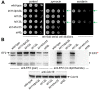
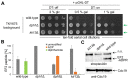
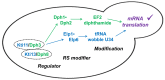
In yeast, Elongator-dependent tRNA modifications are regulated by the Kti11•Kti13 dimer and hijacked for cell killing by zymocin, a tRNase ribotoxin. Kti11 (alias Dph3) also controls modification of elongation factor 2 (EF2) with diphthamide, the target for lethal ADP-ribosylation by diphtheria toxin (DT). Diphthamide formation on EF2 involves four biosynthetic steps encoded by the DPH1-DPH7 network and an ill-defined KTI13 function. On further examining the latter gene in yeast, we found that kti13Δ null-mutants maintain unmodified EF2 able to escape ADP-ribosylation by DT and to survive EF2 inhibition by sordarin, a diphthamide-dependent antifungal. Consistently, mass spectrometry shows kti13Δ cells are blocked in proper formation of amino-carboxyl-propyl-EF2, the first diphthamide pathway intermediate. Thus, apart from their common function in tRNA modification, both Kti11/Dph3 and Kti13 share roles in the initiation step of EF2 modification. We suggest an alias KTI13/DPH8 nomenclature indicating dual-functionality analogous to KTI11/DPH3.
Keywords: EF2 diphthamide modification; budding yeast; diphtheria toxin; elongator; tRNA modification; tRNase zymocin.
Copyright: © 2023 Arend et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: KM and UB are employed by and members of Roche Pharma Research & Early Development, and are co-inventors on patent applications that cover assays to detect presence or absence of diphthamide. Roche is interested in targeted therapies and diagnostics. All other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A versatile partner of eukaryotic protein complexes that is involved in multiple biological processes: Kti11/Dph3.Mol Microbiol. 2008 Sep;69(5):1221-33. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06350.x. Epub 2008 Jul 4. Mol Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18627462
-
Structure of the Kti11/Kti13 heterodimer and its double role in modifications of tRNA and eukaryotic elongation factor 2.Structure. 2015 Jan 6;23(1):149-160. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2014.11.008. Epub 2014 Dec 24. Structure. 2015. PMID: 25543256
-
Yeast alpha-tubulin suppressor Ats1/Kti13 relates to the Elongator complex and interacts with Elongator partner protein Kti11.Mol Microbiol. 2008 Jul;69(1):175-87. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06273.x. Epub 2008 May 5. Mol Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18466297
-
The diphthamide modification pathway from Saccharomyces cerevisiae--revisited.Mol Microbiol. 2014 Dec;94(6):1213-26. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12845. Epub 2014 Nov 17. Mol Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25352115 Review.
-
Diphthamide - a conserved modification of eEF2 with clinical relevance.Trends Mol Med. 2024 Feb;30(2):164-177. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2023.11.008. Epub 2023 Dec 13. Trends Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38097404 Review.
Cited by
-
Diphthamide synthesis is linked to the eEF2-client chaperone machinery.FEBS Lett. 2025 May;599(9):1260-1268. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.15095. Epub 2025 Jan 17. FEBS Lett. 2025. PMID: 39825589 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Integrity of Radical SAM Enzyme Dph1•Dph2 Requires Non-Canonical Cofactor Motifs with Tandem Cysteines.Biomolecules. 2024 Apr 11;14(4):470. doi: 10.3390/biom14040470. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38672486 Free PMC article.
-
DPH1 Gene Mutations Identify a Candidate SAM Pocket in Radical Enzyme Dph1•Dph2 for Diphthamide Synthesis on EF2.Biomolecules. 2023 Nov 16;13(11):1655. doi: 10.3390/biom13111655. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 38002337 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
