Extraction and characterization of a newly developed cellulose enriched sustainable natural fiber from the epidermis of Mikania micrantha
- PMID: 37662786
- PMCID: PMC10469073
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19360
Extraction and characterization of a newly developed cellulose enriched sustainable natural fiber from the epidermis of Mikania micrantha
Abstract
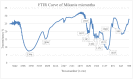
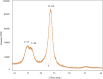
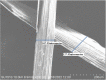
Riding on the journey of a sustainable world it is very crucial to extend the usage of natural cellulosic fiber from renewable sources. Due to their numerous applications and eco-friendly behavior, natural cellulosic fibers are in greater demand every day. In this article a new natural fiber extracted from the creepers of Mikania micrantha with the help of 5% NaOH retting process. Previously no research work have been done with this fiber. The fiber was characterized by following ASTM D1909, ASTM D 2654, ASTM D1445, TAPPI standard for determination of moisture regain and content, bundle fiber strength and chemical composition respectively. XRD, SEM, FTIR and TGA analysis were also done for the identification of crystallinity, fiber morphology, functional group and thermal behavior. The tests results showed that it is a cellulose enriched textile fiber having 56.42% cellulose. The average moisture regain and content % were 9.17% and 8.4% respectively analyzed from the five samples. The average tenacity was determined 38.6 gm/tex with 1.8% elongation and the crystallinity of the tested fiber was 72%. The maximum degradation temperature for this fiber was 477 °C. The application of this noble fiber can be for making fiber reinforced composites, cellulose nanomaterials, biomaterials etc.
Keywords: Cellulose; Mikania micrantha; Retting; Sustainable natural fiber.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Splitting and authentication of the newest retrieved cellulose-rich organic fiber from the exterior layer of Bangladeshi palmyra seed sprouts.RSC Adv. 2024 Sep 24;14(41):30336-30345. doi: 10.1039/d4ra04030a. eCollection 2024 Sep 18. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39318466 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of the physical, chemical and thermal properties of a novel lignocellulosic fiber extracted from the Ravenala madagascariensis leaf stalk.RSC Adv. 2025 Jul 16;15(31):25150-25163. doi: 10.1039/d5ra00644a. eCollection 2025 Jul 15. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40673256 Free PMC article.
-
Extraction and physical characterization of Nymphaea Rubra (water lily) cellulosic fiber for potential textile and green-composite application.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 May;305(Pt 2):141145. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.141145. Epub 2025 Feb 17. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 39971036
-
Durability of Cellulosic-Fiber-Reinforced Geopolymers: A Review.Molecules. 2022 Jan 25;27(3):796. doi: 10.3390/molecules27030796. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35164059 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thermogravimetric Analysis Properties of Cellulosic Natural Fiber Polymer Composites: A Review on Influence of Chemical Treatments.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Aug 13;13(16):2710. doi: 10.3390/polym13162710. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34451248 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Splitting and authentication of the newest retrieved cellulose-rich organic fiber from the exterior layer of Bangladeshi palmyra seed sprouts.RSC Adv. 2024 Sep 24;14(41):30336-30345. doi: 10.1039/d4ra04030a. eCollection 2024 Sep 18. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39318466 Free PMC article.
-
Production of Cellulosic Microfibers from Coffee Pulp via Alkaline Treatment, Bleaching and Acid Hydrolysis.Materials (Basel). 2023 Dec 12;16(24):7607. doi: 10.3390/ma16247607. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38138748 Free PMC article.
-
Plant-Derived Nanocellulose with Antibacterial Activity for Wound Healing Dressing.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Nov 25;15(12):2672. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15122672. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 38140013 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Palamutcu S. Sustainable textile technologies. Textiles and Clothing Sustainability: Sustainable Technologies. 2017:1–22.
-
- Blackburn R. Elsevier; 2009. Sustainable Textiles: Life Cycle and Environmental Impact.
-
- Bright B.M., Selvi B.J., Abu Hassan S., Jaafar M.M., Suchart S., Mavinkere Rangappa S., et al. Characterization of natural cellulosic fiber from cocos nucifera peduncle for sustainable biocomposites. J. Nat. Fibers. 2022;19(14):9373–9383.
-
- Nawaz H., Zhang X., Chen S., You T., Xu F. Recent studies on cellulose-based fluorescent smart materials and their applications: a comprehensive review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021;267 - PubMed
-
- Sgriccia N., Hawley M., Misra M. Characterization of natural fiber surfaces and natural fiber composites. Compos. Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2008;39(10):1632–1637.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

