Adjunctive dexamethasone palmitate use for intercostal nerve block after video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery: A prospective, randomized control trial
- PMID: 37662806
- PMCID: PMC10474424
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19156
Adjunctive dexamethasone palmitate use for intercostal nerve block after video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery: A prospective, randomized control trial
Abstract
Objectives: The efficacy of dexamethasone palmitate in extending durations of local anesthetic blocks is uncertain. In a randomized, double-blind study of patients undergoing video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery, we tested whether intravenous or perineural dexamethasone palmitate caused prolonged analgesia after intercostal nerve block.
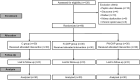
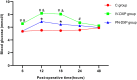
Methods: A total of 90 patients subjected to video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery between May and December 2022 were randomly assigned to one of three intercostal nerve blocks study arms (n = 30 each), requiring the addition of 0.5% ropivacaine (23 ml) as follows: controls (C group), 2 ml saline; IV-DXP group, 2 ml saline + 2 ml (8 mg) intravenous dexamethasone palmitate; and PN-DXP group, 2 ml (8 mg) perineural dexamethasone palmitate. Time to first postoperative remedial analgesia served as primary outcome measure. Secondary endpoints included postoperative opioid consumption, pain scores by Visual Analog Scale, analgesia satisfaction, and related adverse effects.
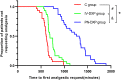
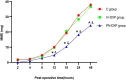
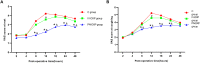
Results: Compared with controls or the IV-DXP group, time to first postoperative remedial analgesia was longer and postoperative opioid consumption for rescue analgesia was lower in the PN-DXP group (p < 0.01). Similarly, the Visual Analog Scale scores in patients at 8, 12, 18, and 24 h postoperatively were lower in the PN-DXP group than in controls and the IV-DXP group (p < 0.01). Patient satisfaction was statistically lower in the PN-DXP group, compared with either the control or IV-DXP group (p < 0.05). Clinically, the three groups did not differ significantly in occurrences of adverse effects during the 48-h postoperative monitoring period (p > 0.05).
Conclusions: Perineural dexamethasone palmitate is a promising adjunct to ropivacaine intercostal nerve block by prolonging analgesia with almost no related adverse effects.
Keywords: Anesthesia; Dexamethasone palmitate; Intercostal nerve block; Postoperative analgesia; Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dexmedetomidine and Dexamethasone as Adjuvants to the Local Anesthetic Mixture in Rhomboid Intercostal and Sub-Serratus Block for Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Controlled Trial.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024 Oct 7;18:4485-4496. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S476929. eCollection 2024. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024. PMID: 39399123 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Ropivacaine with Dexmedetomidine or Dexamethasone in a Thoracic Paravertebral Nerve Block Combined with an Erector Spinae Plane Block for Thoracoscopic Lobectomy Analgesia: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022 May 26;16:1561-1571. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S366428. eCollection 2022. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022. PMID: 35655534 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Dexamethasone and dexmedetomidine as adjuvants to local anesthetic mixture in intercostal nerve block for thoracoscopic pneumonectomy: a prospective randomized study.Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2019 Aug 8:rapm-2018-100221. doi: 10.1136/rapm-2018-100221. Online ahead of print. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2019. PMID: 31399540
-
Efficacy of perineural versus intravenous dexamethasone in prolonging the duration of analgesia when administered with peripheral nerve blocks: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Korean J Anesthesiol. 2022 Jun;75(3):255-265. doi: 10.4097/kja.21390. Epub 2021 Dec 29. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2022. PMID: 34963269 Free PMC article.
-
Perineural dexamethasone added to local anesthesia for brachial plexus block improves pain but delays block onset and motor blockade recovery.Pain Physician. 2015 Jan-Feb;18(1):1-14. Pain Physician. 2015. PMID: 25675053 Review.
Cited by
-
Ultrasound-guided thoracic paravertebral injection of dexamethasone palmitate combined with ropivacaine for the treatment of thoracic herpes zoster-related pain: protocol for a prospective, randomized controlled, single-center study.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jan 7;15:1470772. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1470772. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39872051 Free PMC article.
-
Intravenous injection of dexamethasone is non-inferior to perineural administration for popliteal sciatic nerve and saphenous nerve blocks: A randomized, controlled, triple-blind study.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 24;10(7):e28304. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28304. eCollection 2024 Apr 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38571656 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sheets N.W., Davis J.W., Dirks R.C., et al. Intercostal nerve block with liposomal bupivacaine vs epidural analgesia for the treatment of traumatic rib fracture. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2020;231(1):150–154. 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg. 2019.12.044. - PubMed
-
- Wiles M.D., Nathanson M.H. Local anaesthetics and adjuvants--future developments. Anaesthesia. 2010;65(Suppl 1):22–37. 10.1111/j. 1365-2044.2009.06201.x. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

