The effectiveness of shockwave therapy on patellar tendinopathy, Achilles tendinopathy, and plantar fasciitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 37662911
- PMCID: PMC10468604
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1193835
The effectiveness of shockwave therapy on patellar tendinopathy, Achilles tendinopathy, and plantar fasciitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Tendinopathy is a growing global concern affecting many people, like athletes, workers, and the elderly. Despite its commonality among the sporting population, there is no practical clinical guideline for patellar tendinopathy (PT). Furthermore, there is conflicting evidence between clinical guidelines on shockwave therapy's application and clinical utility for Achilles tendinopathy (AT) and plantar fasciitis (PF). Thus, our aim of this study is to evaluate the evidence for shockwave therapy; to provide a Grading of Recommendation, Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) level of the evidence and effectiveness of shockwave therapy for patellar tendinopathy, Achilles tendinopathy, and Plantar fasciitis.
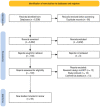
Method: Medical Literature Analysis and Retrieval System Online (Medline), Embase, The Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL), Physiotherapy Evidence Database (PEDro) and China National Knowledge Infrastructure database (CNKI) were searched to find relevant studies published before December 14th, 2022.
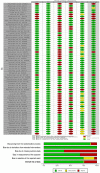
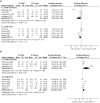
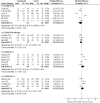
Results: Our study showed that for PT in the short term, extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) or ESWT + eccentric exercise (EE) has a negligible effect on pain and function compared to a placebo or placebo + EE. On the contrary, ESWT significantly affects pain compared to conservative treatment (CT). For AT, ESWT has a small inconclusive effect on pain and function in the short term compared to EE. On the other hand, a placebo outperformed ESWT in improving function for AT but not pain outcomes. PF showed that ESWT significantly affects short- and long-term pain and function. When ESWT was compared to other interventions such as low laser therapy (LLLT), corticosteroid injection (CSI), or CT, there was a small inconclusive effect on pain and function in the short term.
Conclusion: There is low-moderate evidence that ESWT has a negligible effect on pain and function for PT and AT. However, high-quality evidence suggests ESWT has a large effect on pain and function for PF.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?ID=CRD42023396835, identifier CRD42023396835.
Keywords: Achilles tendinopathy; extracorporeal shockwave therapy; patellar tendinopathy; plantar fasciitis; tendinopathy.
Copyright © 2023 Charles, Fang, Zhu and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A Narrative Review Evaluating Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy as a Potential Regenerative Treatment for Musculoskeletal Conditions in Military Personnel.Mil Med. 2021 Jul 1;186(7-8):682-706. doi: 10.1093/milmed/usab106. Mil Med. 2021. PMID: 33770175 Review.
-
The TOPGAME-study: effectiveness of extracorporeal shockwave therapy in jumping athletes with patellar tendinopathy. Design of a randomised controlled trial.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2010 Feb 8;11:28. doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-11-28. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2010. PMID: 20144188 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Effectiveness of Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy for Midportion Achilles Tendinopathy: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2022 Jul 18;14(7):e26960. doi: 10.7759/cureus.26960. eCollection 2022 Jul. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35989757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy for Foot and Ankle Disorders: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2022 May-Jun;112(3):18-191. doi: 10.7547/18-191. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2022. PMID: 34878537
-
No effect of extracorporeal shockwave therapy on patellar tendinopathy in jumping athletes during the competitive season: a randomized clinical trial.Am J Sports Med. 2011 Jun;39(6):1191-9. doi: 10.1177/0363546510395492. Epub 2011 Feb 1. Am J Sports Med. 2011. PMID: 21285447 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Exploring molecular and cellular signaling pathways: Unraveling the pathogenesis of tendinopathy.J Orthop Translat. 2025 Mar 20;51:298-311. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2025.02.003. eCollection 2025 Mar. J Orthop Translat. 2025. PMID: 40201708 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy versus laser therapy in treating musculoskeletal disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Lasers Med Sci. 2025 Apr 15;40(1):194. doi: 10.1007/s10103-025-04392-0. Lasers Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40232318 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of shock wave therapy and ultrasound therapy in non-insertional Achilles tendinopathy: a randomised clinical trial.Front Neurol. 2024 Jul 10;15:1434983. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1434983. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39055323 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Review and Evidence-Based Treatment Framework for Optimizing Plantar Fasciitis Diagnosis and Management.Cureus. 2025 Jul 25;17(7):e88745. doi: 10.7759/cureus.88745. eCollection 2025 Jul. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40717873 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effect of extracorporeal shock-wave therapy on pain in patients with various tendinopathies: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized control trials.BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2024 Apr 24;16(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s13102-024-00884-8. BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2024. PMID: 38659004 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

