Adrenal SGLT1 or SGLT2 as predictors of atherosclerosis under chronic stress based on a computer algorithm
- PMID: 37663275
- PMCID: PMC10474830
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.15647
Adrenal SGLT1 or SGLT2 as predictors of atherosclerosis under chronic stress based on a computer algorithm
Abstract
Background: Chronic stress promotes the development of atherosclerosis, causing disruptions in the body's hormone levels and changes in the structural function of organs.
Objective: The purpose of this study was to investigate the pathological changes in the adrenal gland in a model of atherosclerosis under chronic stress and to verify the expression levels of Sodium-glucose cotransporter (SGLT) 1 and SGLT2 in the adrenal gland and their significance in the changes of adrenal gland.
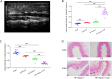
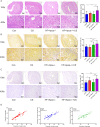
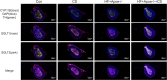
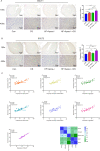
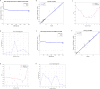
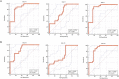
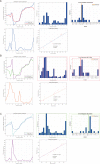
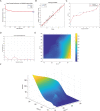
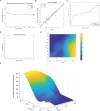
Methods: The model mice were constructed by chronic unpredictable stress, high-fat diet, and Apoe-/- knockout, and they were tested behaviorally at 0, 4, 8 and 12 weeks. The state of the abdominal artery was examined by ultrasound, and the pathological changes of the aorta and adrenal glands were observed by histological methods, and the expression levels and distribution of SGLT1 and SGLT2 in the adrenal gland were observed and analyzed by immunofluorescence and immunohistochemistry. The predictive value of SGLT1 and SGLT2 expression levels on intima-media thickness, internal diameter and adrenal abnormalities were verified by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves, support vector machine (SVM) and back-propagation (BP) neural network.
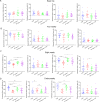
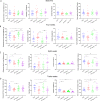
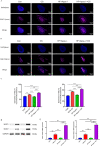
Results: The results showed that chronic stress mice had elevated expression levels of SGLT1 and SGLT2. The model mice developed thickening intima-media and smaller internal diameter in the aorta, and edema, reticular fiber rupture, increased adrenal glycogen content in the adrenal glands. More importantly, analysis of ROC, SVM and BP showed that SGLT1 and SGLT2 expression levels in the adrenal glands could predict the above changes in the aorta and were also sensitive and specific predictors of adrenal abnormalities.
Conclusion: SGLT1 and SGLT2 could be potential biomarkers of adrenal injury in atherosclerosis under chronic stress.
Keywords: Adrenal gland; Atherosclerosis; Chronic stress; Predictors; SGLT1; SGLT2.
©2023 Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SGLT1/2 as the potential biomarkers of renal damage under Apoe-/- and chronic stress via the BP neural network model and support vector machine.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Aug 8;9:948909. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.948909. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36035950 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury under insulin-resistant conditions: SGLT1 but not SGLT2 plays a compensatory protective role in diet-induced obesity.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2019 Jul 1;18(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s12933-019-0889-y. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2019. PMID: 31262297 Free PMC article.
-
SGLT1 in pancreatic α cells regulates glucagon secretion in mice, possibly explaining the distinct effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on plasma glucagon levels.Mol Metab. 2019 Jan;19:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2018.10.009. Epub 2018 Oct 27. Mol Metab. 2019. PMID: 30416006 Free PMC article.
-
The Na+-D-glucose cotransporters SGLT1 and SGLT2 are targets for the treatment of diabetes and cancer.Pharmacol Ther. 2017 Feb;170:148-165. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2016.10.017. Epub 2016 Oct 20. Pharmacol Ther. 2017. PMID: 27773781 Review.
-
Development of SGLT1 and SGLT2 inhibitors.Diabetologia. 2018 Oct;61(10):2079-2086. doi: 10.1007/s00125-018-4654-7. Epub 2018 Aug 22. Diabetologia. 2018. PMID: 30132033 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Particularities of Variation of the Dental Wear in Subjects with Cardiovascular Diseases Compared to Subjects without Systemic Diseases.Curr Health Sci J. 2024 Oct-Dec;50(5):528-545. doi: 10.12865/CHSJ.50.04.07. Epub 2024 Dec 31. Curr Health Sci J. 2024. PMID: 40143882 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bhatt DL, Szarek M, Steg PG, Cannon CP, Leiter LA, McGuire DK, Lewis JB, Riddle MC, Voors AA, Metra M, Lund LH, Komajda M, Testani JM, Wilcox CS, Ponikowski P, Lopes RD, Verma S, Lapuerta P, Pitt B. Sotagliflozin in patients with diabetes and recent worsening heart failure. New England Journal of Medicine. 2021;384:117–128. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2030183. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

