Changes in Healthcare Utilization During the COVID-19 Pandemic and Potential Causes-A Cohort Study From Switzerland
- PMID: 37663371
- PMCID: PMC10469983
- DOI: 10.3389/ijph.2023.1606010
Changes in Healthcare Utilization During the COVID-19 Pandemic and Potential Causes-A Cohort Study From Switzerland
Abstract
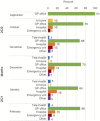
Objectives: To describe the frequency of and reasons for changes in healthcare utilization in those requiring ongoing treatment, and to assess characteristics associated with change, during the second wave of the pandemic. Methods: Corona Immunitas e-cohort study (age ≥20 years) participants completed monthly questionnaires. We compared participants reporting a change in healthcare utilization with those who did not using descriptive and bivariate statistics. We explored characteristics associated with the number of changes using negative binomial regression. Results: The study included 3,190 participants from nine research sites. One-fifth reported requiring regular treatment. Among these, 14% reported a change in healthcare utilization, defined as events in which participants reported that they changed their ongoing treatment, irrespective of the reason. Reasons for change were medication changes and side-effects, specifically for hypertension, or pulmonary embolism treatment. Females were more likely to report changes [Incidence Rate Ratio (IRR) = 2.15, p = 0.002]. Those with hypertension were least likely to report changes [IRR = 0.35, p = 0.019]. Conclusion: Few of those requiring regular treatment reported changes in healthcare utilization. Continuity of care for females and chronic diseases besides hypertension must be emphasized.
Keywords: COVID-19; digital follow-up; healthcare delivery; healthcare utilization; population-based study.
Copyright © 2023 Harju, Speierer, Jungo, Levati, Baggio, Tancredi, Noor, Rodondi, Cullati, Imboden, Keidel, Witzig, Frank, Kohler, Kahlert, Crivelli, Amati, Albanese, Kaufmann, Frei, von Wyl, Puhan, Probst-Hensch, Michel, Rodondi and Chocano-Bedoya.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they do not have any conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Wirth B, Stucki M, Jörg R, Thommen C, Pahud O, Höglinger M. Die Schweizer Spitäler in der Covid-19-Pandemie. Auswirkungen auf die Fallzahlen der stationären Gesundheitsversorgung. Neuchâtel: Schweizerisches Gesundheitsobservatorium; (2022).

