Clarithromycin-induced acute liver injury in a patient with positive Helicobacter pylori: a case report and review of the literature
- PMID: 37663679
- PMCID: PMC10473337
- DOI: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000001135
Clarithromycin-induced acute liver injury in a patient with positive Helicobacter pylori: a case report and review of the literature
Abstract
Introduction and importance: While 14-day triple therapy with clarithromycin is a common approach for eradicating Helicobacter pylori infection, it is essential to note that this treatment does not come without potential side effects.
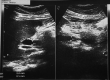
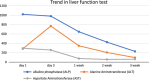
Case presentation: We present the case of a 34-year-old male who presented to the emergency department with severe vomiting and abdominal pain. Subsequent evaluation revealed that the patient had developed drug-induced liver injury (DILI).
Clinical discussion: DILI can cause acute hepatocellular or cholestatic damage, and chronic injury can lead to hepatocellular, cholestatic, vascular, or neoplastic manifestations.
Conclusion: Clinicians should exercise caution and be alert to the potential hepatotoxic effects of medications, especially when initiating triple therapy for H. pylori infection.
Keywords: Helicobacter pylori; clarithromycin; drug-induced liver injury.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.Sponsorships or competing interests that may be relevant to content are disclosed at the end of this article.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources