Physicians' perspectives on different therapeutic approaches for aluminum phosphide poisoning and their relevant outcomes
- PMID: 37663810
- PMCID: PMC10470372
- DOI: 10.1093/toxres/tfad053
Physicians' perspectives on different therapeutic approaches for aluminum phosphide poisoning and their relevant outcomes
Abstract
Background: Aluminum phosphide is a highly toxic pesticide that results in high mortality. To date, there is neither a definitive antidote nor a unified protocol for managing acute aluminum phosphide poisoning.
Objectives: This cross-sectional questionnaire-based study aims to explore different management approaches and rely on the expertise of Egyptian medical professionals to enhance the prognosis for acute aluminum phosphide poisoning.
Subjects and methods: A self-administered questionnaire was formulated and electronically distributed according to published literature and experience of senior physicians.
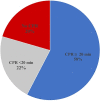
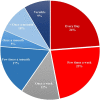
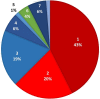
Results and conclusions: Responses were received from 151 physicians from 10 governorates. Management modalities were variable among respondents. Noradrenaline was used by 90.7% of respondents with no fixed-dose regimen. In all, 84.1% of participants utilized oil in gastrointestinal decontamination; paraffin oil was the most used solution. Overall, 92.1, 61.6, 46.4, and 34.4% of participants used sodium bicarbonate, proton pump inhibitors, IV magnesium sulfate, and antioxidants, respectively. Regarding the frequency of acute aluminum phosphide poisoning, 47% of participants managed these cases daily or a few times a week. Participants' responses denoted a poor prognosis of acute aluminum phosphide poisoning, and high percentages attributed the prognosis to exposure factors rather than treatment modalities. Statistical analysis revealed that using oil in gastrointestinal decontamination improved the outcome by 4.62-fold. Clinical toxicologists were more likely to rescue ≥ 30% of the cases about 3-fold (2.97) than other specialties. Clinical toxicologists used oil in gastrointestinal decontamination, magnesium sulfate, and antioxidant therapy and calculated base deficit before administration of sodium bicarbonate by 7.70-, 5.30-, 3.26-, and 2.08-fold than other specialties.
Keywords: Egypt; acute poisoning; aluminum phosphide; clinical toxicologist.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Potential role of paraffin oil gastric lavage in acute aluminum phosphide poisoning: a randomized controlled trial.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022 May;29(22):33844-33855. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-17778-8. Epub 2022 Jan 15. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35031985 Clinical Trial.
-
The efficacy of Coenzyme Q10 and liquid paraffin oil in the management of acute aluminum phosphide poisoning.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2020 Jul 2;9(4):444-453. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfaa045. eCollection 2020 Jul. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2020. PMID: 33936588 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing the effectiveness of L-carnitine and paraffin oil in acute aluminum phosphide poisoning using predictive biomarkers and scores: A randomized controlled clinical trial.Hum Exp Toxicol. 2023 Jan-Dec;42:9603271221149650. doi: 10.1177/09603271221149650. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 36592154 Clinical Trial.
-
Management of Acute Aluminum Phosphide Poisoning: Has Anything Changed?Drug Metab Lett. 2021;14(2):106-116. doi: 10.2174/1872312814666210813115625. Drug Metab Lett. 2021. PMID: 34818996 Review.
-
[Progress in treatment of acute aluminum phosphide poisoning].Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2019 Nov 20;37(11):877-880. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-9391.2019.11.021. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31838827 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
The therapeutic effect of a novel parenteral formulation of dihydroxyacetone in aluminum phosphide-intoxicated patients.Heliyon. 2023 Nov 10;9(11):e22165. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e22165. eCollection 2023 Nov. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38053886 Free PMC article.
-
Medicolegal analysis of physical violence toward physicians in Egypt.Sci Rep. 2024 May 13;14(1):10911. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-60857-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38740880 Free PMC article.
-
Arterial blood gases and serum cortisol level as predictors for mortality in acute aluminum phosphide poisoned patients: A prospective cohort study.Toxicol Rep. 2024 Dec 17;14:101865. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2024.101865. eCollection 2025 Jun. Toxicol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39802601 Free PMC article.
-
Aluminum phosphide: Toxicological profiles, health risks, environmental impact, and management protocols: A review.Turk J Emerg Med. 2025 Jul 1;25(3):178-190. doi: 10.4103/tjem.tjem_49_25. eCollection 2025 Jul-Sep. Turk J Emerg Med. 2025. PMID: 40746573 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of a risk-prediction nomogram for in-hospital adverse cardiovascular events in acute cardiotoxic agents poisoning.Toxicol Rep. 2024 Nov 20;13:101826. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2024.101826. eCollection 2024 Dec. Toxicol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39654999 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Armandeh M, Bameri B, Baeeri M, Haghi-Aminjan H, Rahimifard M, Hassani S, Hooshangi Shayesteh MR, Khalid M, Samadi M, Hosseini R, et al. . The role of levosimendan in phosphine-induced cardiotoxicity: evaluation of electrocardiographic, echocardiographic, and biochemical parameters. Toxicol Mech Methods. 2021:31(9):631–643. - PubMed
-
- Helal N, Lashin H, Nagy A, Shama M, Mostafa T, Wahdan A. Potential role of paraffin oil gastric lavage in acute aluminum phosphide poisoning: a randomized controlled trial. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2022:29(22):33844–33855. - PubMed
-
- Zaki MK, Sobh ZK. Optimum standardization of healthcare medicolegal reports in Egypt: a forensic medicine initiative. Forensic Sci Int Rep. 2022:5:100255.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

