The most common pulmonary diseases length of stay, and characteristics of patients admitted to pulmonary service
- PMID: 37663882
- PMCID: PMC10473058
- DOI: 10.4103/atm.atm_348_22
The most common pulmonary diseases length of stay, and characteristics of patients admitted to pulmonary service
Abstract
Background: Although chronic respiratory diseases are prevalent in Saudi Arabia, there are limited data on the patient burden and associated factors. The aim of this study is to identify the chronic respiratory diseases frequently admitted to pulmonary services and to determine the patient's characteristics, associated comorbidities readmission rate, and reason for a more extended stay in hospital.
Methods: A prospective study was conducted over a 5-year period at King Abdulaziz Medical City-Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, in the Pulmonary Division, between March 2015 and December 2019. Data on demographics, comorbidities, and chronic respiratory diseases were collected.
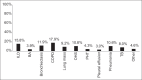
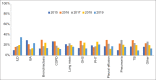
Results: Total patients admitted were 1315 patients, female 54.2%, the mean age was 62.4 (SD±17.6), and the ages ranged from 14 to 98 years. Overall, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease was the most common respiratory disease requiring admission (17.9%), followed by interstitial lung disease (15.8%), bronchiectasis (11.9%), and obesity hypoventilation syndrome (10.8%). The most common comorbidities were obesity (42.5%), diabetes 49.1%, and hypertension 54.9%. Only 135 (10.3%) were readmitted within 30 days posthospital discharge. Among the patients who were readmitted, 103 (76.3%) were readmitted due to issues related to previous admission diagnosis, noncompliance 75 (55.5%), social reasons, and premature discharges in 51 (37.8%) and 29 (21.5%) of the cases, respectively. The respiratory disease varied significantly by gender, age, obesity status, comorbidities, length of stay (LOS), and admissions.
Conclusion: Chronic respiratory diseases are prevalent in our population and are mainly influenced by gender, age, obesity status, comorbidities, LOS, and admissions. Policymakers and health professionals need to recognize the burden of chronic respiratory diseases on patients and health systems and implement effective prevention programs.
Keywords: Burden; chronic respiratory diseases; comorbidities; length of stay.
Copyright: © 2023 Annals of Thoracic Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: influence of social factors in determining length of hospital stay and readmission rates.Can Respir J. 2008 Oct;15(7):361-4. doi: 10.1155/2008/569496. Can Respir J. 2008. PMID: 18949105 Free PMC article.
-
Longer length of stay, days between discharge/first readmission, and pulmonary involvement ≥50% increase prevalence of admissions in ICU in unplanned readmissions after COVID-19 hospitalizations.J Med Virol. 2022 Aug;94(8):3750-3756. doi: 10.1002/jmv.27792. Epub 2022 May 4. J Med Virol. 2022. PMID: 35506668 Free PMC article.
-
Demographic Characteristics, Comorbidities, and Length of Stay of COVID-19 Patients Admitted Into Intensive Care Units in Saudi Arabia: A Nationwide Retrospective Study.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jul 13;9:893954. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.893954. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35911421 Free PMC article.
-
Factors associated with hospital stay length, discharge destination, and 30-day readmission rate after primary hip or knee arthroplasty: Retrospective Cohort Study.Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2019 Sep;105(5):949-955. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2019.04.012. Epub 2019 Jun 15. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2019. PMID: 31208932 Review.
-
The respiratory rehabilitation Maugeri network service reconfiguration after 1 year of COVID-19.Monaldi Arch Chest Dis. 2021 Jun 8;91(4). doi: 10.4081/monaldi.2021.1843. Monaldi Arch Chest Dis. 2021. PMID: 34935324 Review.
Cited by
-
The Saudi initiative for asthma - 2024 update: Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of asthma in adults and children.Ann Thorac Med. 2024 Jan-Mar;19(1):1-55. doi: 10.4103/atm.atm_248_23. Epub 2023 Dec 15. Ann Thorac Med. 2024. PMID: 38444991 Free PMC article.
-
Hospital readmission after an acute admission to internal medicine: Causes and risk factors in a tertiary care center in Saudi Arabia.Saudi Med J. 2025 Mar;46(3):261-268. doi: 10.15537/smj.2025.46.3.20240689. Saudi Med J. 2025. PMID: 40096974 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burney P, Jarvis D, Perez-Padilla R. The global burden of chronic respiratory disease in adults. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2015;19:10–20. - PubMed
-
- World health organization. The top 10 causes of death. [[Last accessed on 2022 Aug 01]]. URL: Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death .
-
- Tageldin MA, Nafti S, Khan JA, Nejjari C, Beji M, Mahboub B, et al. Distribution of COPD-related symptoms in the Middle East and North Africa: Results of the BREATHE study. Respir Med. 2012;106(Suppl 2):S25–32. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources