Assessing the Knowledge and Practices of Burn First Aid in Al-Baha Region, Saudi Arabia
- PMID: 37664287
- PMCID: PMC10474332
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.42879
Assessing the Knowledge and Practices of Burn First Aid in Al-Baha Region, Saudi Arabia
Abstract
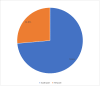
Background Burns are a prevalent type of injury that can result in substantial morbidity and mortality. Burn first aid knowledge is essential for reducing its complications and improving outcomes. However, evidence of the amount of burn first aid knowledge among the general population in many nations is sparse. Methodology A cross-sectional survey was conducted among 346 persons over the age of 18 from the Al-Baha region of Saudi Arabia. The participants' knowledge of first aid for burns, including the appropriate steps to take in the event of a burn, the types of burns, and the proper application of burn dressings was assessed using a structured questionnaire. Results The majority of participants (73.6%) had inadequate knowledge of first aid for burns, while only 26.4% had adequate knowledge. The most common misconception among participants was the use of toothpaste, honey, or ice for burn treatment, which is not recommended. Additionally, hot water was the main cause of burning in this study. Conclusions This study underscores the necessity for targeted education and awareness-raising activities to improve the general population's knowledge and habits about first aid for burns. Such programs can be tailored to clarify myths and misunderstandings regarding burn treatment and encourage evidence-based strategies for preventing and treating burns.
Keywords: al-baha; assessing; awareness; burn; first aid; knowledge.
Copyright © 2023, Asiri et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Prevention of burn injuries in low- and middle-income countries: a systematic review. Rybarczyk MM, Schafer JM, Elm CM, et al. Burns. 2016;42:1183–1192. - PubMed
-
- Epidemiology of burn injury and the ideal dressing in global burn care - regional differences explored. Opriessnig E, Luze H, Smolle C, et al. Burns. 2023;49:1–14. - PubMed
-
- The epidemiology of burn injuries in Saudi Arabia: a systematic review. Almarghoub MA, Alotaibi AS, Alyamani A, Alfaqeeh FA, Almehaid FF, Al-Qattan MM, Kattan AE. J Burn Care Res. 2020;41:1122–1127. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources