Epidemiological Correlates of Substance Abuse Among In-Facility Clients of De-addiction and Rehabilitation Centres of District Dehradun: A Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 37664384
- PMCID: PMC10471516
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.42826
Epidemiological Correlates of Substance Abuse Among In-Facility Clients of De-addiction and Rehabilitation Centres of District Dehradun: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
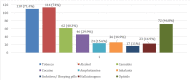
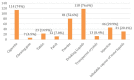
Background The increasing production, distribution, promotion, and availability of substances contemporaneous with the changing values of society have resulted in rising substance abuse as an emerging public health concern in India. A prevalence of 32-37% has been reported for substance abuse in various studies conducted in Uttarakhand but there is a dearth of data on socio-epidemiological factors affecting substance abuse. Materials & methods A facility-based observational cross-sectional study was conducted in selected de-addiction and rehabilitation centers of district Dehradun. Data were collected using multistage systematic random sampling from clients admitted to the facility. Results The mean age of in-facility participants was 28 ± 8 years and most of them started taking drugs after the age of 18 years. The most common substance of abuse was alcohol (61.7%) followed by tobacco smoking (15.6%). Both 'peer pressure' and 'curiosity' play a major role in predisposition to substance use. Further, we found that age (p=0.002), and level of education (p <0.001) were important determinants for substance abuse. At the same time, among other factors, the influence of occupation notably did not have a statistically significant association. Conclusion Sensitization and capacity building of both providers and the community is integral to effective strategizing for the prevention and control of substance abuse. Regional studies including the current study can be of help in framing drug policies and management guidelines including prioritizing the importance of the establishment of de-addiction and rehabilitation centers at the district level.
Keywords: addiction; alcohol; de-addiction centres; socio-demographic variables; substance abuse.
Copyright © 2023, Zahin et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Substance abuse among Adolescents and Youth (10-24 years): Assessing the prevalence and risk assessment in the suburban areas of Dehradun District, Uttarakhand.J Family Med Prim Care. 2025 Mar;14(3):954-962. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_1260_24. Epub 2025 Mar 25. J Family Med Prim Care. 2025. PMID: 40256096 Free PMC article.
-
Rising trend of substance abuse in Pakistan: a study of sociodemographic profiles of patients admitted to rehabilitation centres.Public Health. 2019 Feb;167:34-37. doi: 10.1016/j.puhe.2018.10.020. Epub 2019 Jan 4. Public Health. 2019. PMID: 30616031
-
Sociodemographic and substance use correlates of repeated relapse among patients presenting for relapse treatment at an addiction treatment center in Kolkata, India.Afr Health Sci. 2013 Sep;13(3):791-9. doi: 10.4314/ahs.v13i3.39. Afr Health Sci. 2013. PMID: 24250323 Free PMC article.
-
Profile of Psychosocial Rehabilitation Centres for Persons with Substance Use Disorders in Bengaluru: A Cross-Sectional Study.J Psychosoc Rehabil Ment Health. 2022;9(3):293-302. doi: 10.1007/s40737-022-00265-9. Epub 2022 Mar 22. J Psychosoc Rehabil Ment Health. 2022. PMID: 35342688 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding the neurobiology, assessment, and treatment of substances of abuse and dependence: a guide for the critical care nurse.Crit Care Nurs Clin North Am. 2012 Mar;24(1):117-30. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2012.01.007. Crit Care Nurs Clin North Am. 2012. PMID: 22405717 Review.
Cited by
-
Substance abuse among Adolescents and Youth (10-24 years): Assessing the prevalence and risk assessment in the suburban areas of Dehradun District, Uttarakhand.J Family Med Prim Care. 2025 Mar;14(3):954-962. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_1260_24. Epub 2025 Mar 25. J Family Med Prim Care. 2025. PMID: 40256096 Free PMC article.
References
-
- National Survey on extent, patterns and trends of drug abuse in India 2003-a report. [ Jul; 2023 ]. 2004. https://www.unodc.org/pdf/india/presentations/india_national_survey_2004... https://www.unodc.org/pdf/india/presentations/india_national_survey_2004...
-
- Guidelines for the identification and management of substance use and substance use disorders . [ Jul; 2023 ];https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/107130/9789241548731_en... 2014 48 - PubMed
-
- Magnitude of substance use. Ambekar A, Chadda RK, Khandelwal SK, et al. https://www.muktangan.org/pdf/Magnitude_Substance_Use_India_REPORT.pdf Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment. 2019
-
- Prevalence of substance abuse in Rishikesh: a community based study. Kumar D, Kishore S, Khapre M, Usha P, Rehan A, Reddy NK. National Journal of Community Medicine. 2020
-
- Practices & socio-cultural aspects of substance use among residents of a newly formed state: A cross sectional study in Dehradun. . Varshney DS, Semwal J, Srivastava AK, Vyas S, Sati H. https://njmr.in/index.php/file/article/view/544 NJMR. 2014;4:330–336.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources