Genome-wide association study identifies several loci for HEV seropositivity
- PMID: 37664632
- PMCID: PMC10470371
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107586
Genome-wide association study identifies several loci for HEV seropositivity
Abstract
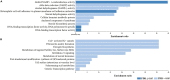
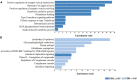
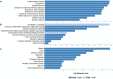
Hepatitis E viral (HEV) infection imposes a heavy global health burden. The variability in the prevalence of serological markers of HEV infection between different ethnic groups proposes a host genetic influence. Here, we report genetic polymorphisms associated with anti-HEV antibody positivity and level using binary- and quantitative-trait genome-wide association studies (GWAS) on a population from Qatar (n = 5829). We identified a region in 12p11.1 (lead SNP: rs559856097, allele: A, p = 2.3 × 10-10) significantly associated with anti-HEV antibodies level. This intergenic variant is located near SNORD112, a small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA). Additional gene-set and pathway enrichment analyses highlighted a strong correlation with anti-viral response-related pathways, including IFNs (alpha/beta) and interleukin-21 (IL-21) signaling. This is the first GWAS on the response to HEV infection. Further replication and functional experimentation are warranted to validate these findings.
Keywords: Association analysis; Immune response; Quantitative genetics; Virology.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
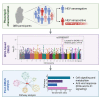
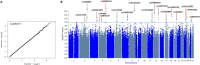
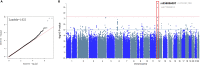

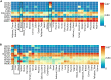
References
-
- Hepatitis E. 2022. https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-e
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

