Reproducibility and location-stability of radiomic features derived from cone-beam computed tomography: a phantom study
- PMID: 37664997
- PMCID: PMC10968769
- DOI: 10.1259/dmfr.20230180
Reproducibility and location-stability of radiomic features derived from cone-beam computed tomography: a phantom study
Abstract
Objectives: This study aims to determine the reproducibility and location-stability of cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) radiomic features.
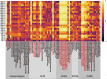
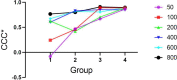
Methods: Centrifugal tubes with six concentrations of K2HPO4 solutions (50, 100, 200, 400, 600, and 800 mg ml-1) were imaged within a customized phantom. For each concentration, images were captured twice as test and retest sets. Totally, 69 radiomic features were extracted by LIFEx. The reproducibility was assessed between the test and retest sets. We used the concordance correlation coefficient (CCC) to screen qualified features and then compared the differences in the numbers of them under 24 series (four locations groups * six concentrations). The location-stability was assessed using the Kruskal-Wallis test under different concentration sets; likewise, the numbers of qualified features under six test sets were analyzed.
Results: There were 20 and 23 qualified features in the reproducibility and location-stability experiments, respectively. In the reproducibility experiment, the performance of the peripheral groups and high-concentration sets was significantly better than the center groups and low-concentration sets. The effect of concentration on the location-stability of features was not monotonic, and the number of qualified features in the low-concentration sets was greater than that in the high-concentration sets. No features were qualified in both experiments.
Conclusions: The density and location of the target object can affect the number of reproducible radiomic features, and its density can also affect the number of location-stable radiomic features. The problem of feature reliability should be treated cautiously in radiomic research on CBCT.
Keywords: Cone-Beam Computed Tomography; Location-stability; Phantom Study; Radiomic Features; Reproducibility.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of reproducible radiomic features from on-board volumetric images: A multi-institutional phantom study.Med Phys. 2023 Sep;50(9):5585-5596. doi: 10.1002/mp.16376. Epub 2023 Mar 24. Med Phys. 2023. PMID: 36932977
-
Repeatability of CBCT radiomic features and their correlation with CT radiomic features for prostate cancer.Med Phys. 2021 May;48(5):2386-2399. doi: 10.1002/mp.14787. Epub 2021 Mar 16. Med Phys. 2021. PMID: 33598943
-
Can radiomics features be reproducibly measured from CBCT images for patients with non-small cell lung cancer?Med Phys. 2015 Dec;42(12):6784-97. doi: 10.1118/1.4934826. Med Phys. 2015. PMID: 26632036 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Cone-beam computed-tomography-based delta-radiomic analysis for investigating prognostic power for esophageal squamous cell cancer patients undergoing concurrent chemoradiotherapy.Phys Med. 2024 Jan;117:103182. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmp.2023.103182. Epub 2023 Dec 12. Phys Med. 2024. PMID: 38086310
-
Assessing the reproducibility of CBCT-derived radiomics features using a novel three-dimensional printed phantom.Med Phys. 2021 Aug;48(8):4326-4333. doi: 10.1002/mp.15043. Epub 2021 Jul 11. Med Phys. 2021. PMID: 34120354
Cited by
-
Photon-Counting CT Scan Phantom Study: Stability of Radiomics Features.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Mar 7;15(6):649. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15060649. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40149992 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bianchi J, Gonçalves JR, de Oliveira Ruellas AC, Ashman LM, Vimort J-B, Yatabe M, et al. . Quantitative bone imaging biomarkers to diagnose Temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis. International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 2021; 50: 227–35. doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2020.04.018 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

