Essential steps in primary care management of older people with Type 2 diabetes: an executive summary on behalf of the European geriatric medicine society (EuGMS) and the European diabetes working party for older people (EDWPOP) collaboration
- PMID: 37665557
- PMCID: PMC10628003
- DOI: 10.1007/s40520-023-02519-3
Essential steps in primary care management of older people with Type 2 diabetes: an executive summary on behalf of the European geriatric medicine society (EuGMS) and the European diabetes working party for older people (EDWPOP) collaboration
Abstract
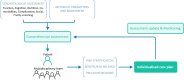
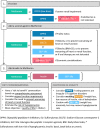
We present an executive summary of a guideline for management of type 2 diabetes mellitus in primary care written by the European Geriatric Medicine Society, the European Diabetes Working Party for Older People with contributions from primary care practitioners and participation of a patient's advocate. This consensus document relies where possible on evidence-based recommendations and expert opinions in the fields where evidences are lacking. The full text includes 4 parts: a general strategy based on comprehensive assessment to enhance quality and individualised care plan, treatments decision guidance, management of complications, and care in case of special conditions. Screening for frailty and cognitive impairment is recommended as well as a comprehensive assessment all health conditions are concerned, including end of life situations. The full text is available online at the following address: essential_steps_inprimary_care_in_older_people_with_diabetes_-_EuGMS-EDWPOP___3_.pdf.
Keywords: Cognitive disorders; Frailty; Glucose lowering therapy; Integrative care; Prevention; Type diabetes mellitus.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have declared a Conflict of Interest in this manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Bourdel MI. Models of care, the European perspective. In: Sinclair AJ, editor. Diabetes Old age. Chippenham: Wiley-Blackwell; 2009. pp. 453–459.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical