Using a chat-based informed consent tool in large-scale genomic research
- PMID: 37665746
- PMCID: PMC10797258
- DOI: 10.1093/jamia/ocad181
Using a chat-based informed consent tool in large-scale genomic research
Abstract
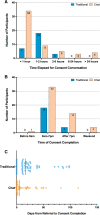
Objective: We implemented a chatbot consent tool to shift the time burden from study staff in support of a national genomics research study.
Materials and methods: We created an Institutional Review Board-approved script for automated chat-based consent. We compared data from prospective participants who used the tool or had traditional consent conversations with study staff.
Results: Chat-based consent, completed on a user's schedule, was shorter than the traditional conversation. This did not lead to a significant change in affirmative consents. Within affirmative consents and declines, more prospective participants completed the chat-based process. A quiz to assess chat-based consent user understanding had a high pass rate with no reported negative experiences.
Conclusion: Our report shows that a structured script can convey important information while realizing the benefits of automation and burden shifting. Analysis suggests that it may be advantageous to use chatbots to scale this rate-limiting step in large research projects.
Keywords: chatbot; genetic counseling; genomics; informed consent; large-scale research.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the American Medical Informatics Association.
Conflict of interest statement
EDS, SKS, GM, AHKK, RN, and VAF were full time employees and stockholders of Invitae Corporation at the time of the study.
Figures