The bidirectional relationship between Alzheimer's disease (AD) and epilepsy: A Mendelian randomization study
- PMID: 37666799
- PMCID: PMC10636418
- DOI: 10.1002/brb3.3221
The bidirectional relationship between Alzheimer's disease (AD) and epilepsy: A Mendelian randomization study
Abstract
Background: There is a complex, bidirectional relationship between Alzheimer's disease (AD) and epilepsy. However, the causality of this association is unclear, as confounders play a role in this association.
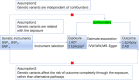
Methods: We conducted a Mendelian randomization (MR) study to clarify the causal relationship and direction of epilepsy on AD risk. We used publicly available summary statistics to obtain all genetic datasets for the MR analyses. AD and AD-by-proxy and late-onset AD (LOAD) cohorts were included in our study. The epilepsy cohort comprised all epilepsy, generalized epilepsy, focal epilepsy, and its subtypes, as well as some epilepsy syndromes. Next, we conducted validation using another AD cohort.
Results: Two correlations between AD and epilepsy using the inverse variance-weighted (IVW) method are as follows: LOAD and focal epilepsy (ORIVW = 1.079, pIVW = .013), focal epilepsy-documented hippocampal sclerosis (HS) and AD (ORIVW = 1.152, pIVW = .017). The causal relationship between epilepsy-documented HS and AD has been validated (ORIVW = 3.994, pIVW = .027).
Conclusions: Our MR study provides evidence for a causal relationship between focal epilepsy-documented HS and AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Alzheimer's disease (late onset) (load); Mendelian randomization; epilepsy; focal epilepsy.
© 2023 The Authors. Brain and Behavior published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Bellenguez, C. , Küçükali, F. , Jansen, I. E. , Kleineidam, L. , Moreno‐Grau, S. , Amin, N. , Naj, A. C. , Campos‐Martin, R. , Grenier‐Boley, B. , Andrade, V. , Holmans, P. A. , Boland, A. , Damotte, V. , Van Der Lee, S. J. , Costa, M. R. , Kuulasmaa, T. , Yang, Q. , De Rojas, I. , Bis, J. C. , … Lambert, J.‐C. (2022). New insights into the genetic etiology of Alzheimer's disease and related dementias. Nature Genetics, 54(4), 412–436. 10.1038/s41588-022-01024-z - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

