2DeteCT - A large 2D expandable, trainable, experimental Computed Tomography dataset for machine learning
- PMID: 37666897
- PMCID: PMC10477177
- DOI: 10.1038/s41597-023-02484-6
2DeteCT - A large 2D expandable, trainable, experimental Computed Tomography dataset for machine learning
Abstract
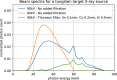
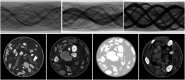
Recent research in computational imaging largely focuses on developing machine learning (ML) techniques for image reconstruction, which requires large-scale training datasets consisting of measurement data and ground-truth images. However, suitable experimental datasets for X-ray Computed Tomography (CT) are scarce, and methods are often developed and evaluated only on simulated data. We fill this gap by providing the community with a versatile, open 2D fan-beam CT dataset suitable for developing ML techniques for a range of image reconstruction tasks. To acquire it, we designed a sophisticated, semi-automatic scan procedure that utilizes a highly-flexible laboratory X-ray CT setup. A diverse mix of samples with high natural variability in shape and density was scanned slice-by-slice (5,000 slices in total) with high angular and spatial resolution and three different beam characteristics: A high-fidelity, a low-dose and a beam-hardening-inflicted mode. In addition, 750 out-of-distribution slices were scanned with sample and beam variations to accommodate robustness and segmentation tasks. We provide raw projection data, reference reconstructions and segmentations based on an open-source data processing pipeline.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Lecun Y, Bottou L, Bengio Y, Haffner P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proceedings of the IEEE. 1998;86:2278–2324. doi: 10.1109/5.726791. - DOI
-
- Deng, J. et al. Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 248–255, 10.1109/CVPR.2009.5206848 (2009).
-
- McCollough C. Tu-fg-207a-04: overview of the low dose ct grand challenge. Medical physics. 2016;43:3759–3760.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

