Perceived stress reduction through an infertility coaching program: a randomized controlled clinical trial
- PMID: 37666933
- PMCID: PMC10477300
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-41845-4
Perceived stress reduction through an infertility coaching program: a randomized controlled clinical trial
Abstract
Infertility has been recognized as a distressing experience among couples worldwide, cutting across various cultures. This present study was conducted to assess the impact of a supportive stress management program led by an infertility coach for women undergoing fertility treatment. This randomized controlled clinical trial study was performed on 60 infertile women undergoing assisted reproductive techniques at Maryam Infertility Center located in Sari in 2018. After random allocation in two groups, 30 individuals were in the intervention group and 30 in the control group. The intervention program was implemented according to the infertility coach's counseling protocol in six stages. The control group received only routine ward counseling. In order to measure stress, the Newton Infertility Stress Questionnaire was used firstly before intervention and then after oocyte puncture, embryo transfer, and pregnancy testing. Data analysis was performed using SPSS statistical software version 18 and Shapiro-Wilk, Chi-square, Mann-Whitney, independent t-test, Friedman test, Wilcoxon test, GEE test, and Cohen's effect size. Our analysis approach has also been based on the analysis of (ITT). The significance level was 0.05. The mean ± SD scores of infertility perceived stress before the intervention in the control was 146.16 ± 16.90 and the intervention group was 156.53 ± 9.31, after intervention at the time of oocyte puncture in the controls was 165.36 ± 8.98 and the intervention group was 155.83 ± 10.70, at the day of embryo transfer in the control group was 156.35 ± 14.45 and in the intervention group was 123.58 ± 22.9 and in the pregnancy test day in the control group was 185.76 ± 26.56 and in the intervention group was 127.61 ± 21.57 (P < 0.001). According to Friedman test, the mean of stress in three situations after the intervention showed a significant difference in reduction of the mean of stress (P < 0.001). In the control group, the stress score of the samples had an increasing trend, which was significant during the measurement steps based on Friedman test results (P < 0.001). In the intervention group, paired t-test results showed no significant comparing mean score of Newton's infertility stress before and after oocyte puncture day (P = 0.711), comparing the mean of stress before and after pregnancy test day (P = 0.003) and also comparing of mean stress before and after pregnancy on the day of embryo transfer according to Wilcoxon test (P < 0.001). And comparing mean stress before and after pregnancy test day, paired t-test (P = 0.001) showed significant statistical differences. According to the results of the GEE test, changes in stress scores over time were significant between the two groups (P < 0.001), as well as the effect of stress on oocyte puncture day (0.41), embryo transfer day (1.69), pregnancy test day (P < 0.001) (2.46) had a significant effect on the day of embryo transfer and pregnancy test day. Based on the results of this study, the infertility coach program demonstrated the ability to decrease the perceived stress related to infertility. Additionally, it showed potential in enhancing treatment outcomes, such as oocyte count and positive pregnancy results, among infertile women undergoing assisted reproductive techniques.Trial registration: Iranian Registry for Clinical Trial (the link to trial: https://www.irct.ir/trial/33357 ). Registered 11-11-2018.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
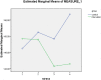
References
-
- Berek JS. Berek & Novak Gynecology. Golban; 2007.
-
- Gallinelli A, Roncaglia R, Matteo ML, Ciaccio I, Volpe A, Facchinetti F. Immunological changes and stress are associated with different implantation rates in patients undergoing in vitro fertilization–embryo transfer. Fertil. Steril. 2001;76(1):85–91. doi: 10.1016/S0015-0282(01)01826-X. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gardner DK, Weissman A, Howles CM, Shoham Z. Textbook of Assisted Reproductive Techniques Fourth Edition: Volume 2: Clinical Perspectives. CRC Press; 2012.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

