Enzyme cocktail with hyperactive lipase through solid-state fermentation by the novel strain Penicillium sp. Y-21
- PMID: 37667063
- PMCID: PMC10477218
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-41912-w
Enzyme cocktail with hyperactive lipase through solid-state fermentation by the novel strain Penicillium sp. Y-21
Abstract
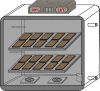
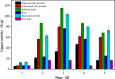
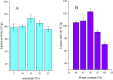
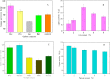
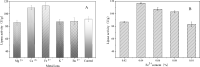
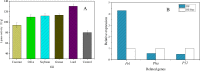
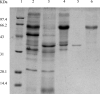
Lipase is a kind of industrial enzyme preparation with various catalytic abilities and is widely used in food, energy, medicine and other fields. To increase lipase and enzyme cocktail activity through solid-state fermentation, the novel strain Penicillium sp. Y-21 was obtained through ethyl methanesulfonate (EMS) mutation from the novel strain Y, which was isolated from soils. Solid-state fermentation by strain Y-21 using agricultural byproducts was carried out in tray bioreactors. The optimum culture composition for enzyme cocktail fermentation was soybean meal 20 g, 3% (w/w) glucose, 1% (w/w) peptone, 5% (w/w) lard, 0.04% (w/w) CaCl2, 0.04% (w/w) FeCl3, 28 °C for 72 h. The enzyme cocktail produced by strain Y-21 is a kind of multienzyme complex, containing xylanase, glucanase, acidic protease, pectinase, cellulase and lipase, and their enzymatic activities (unit: U g-1) were 8000, 6000, 8000, 2000, 3000 and 120, respectively. During the fermentation process, the lipase coding genes pel, pha, and p12 were also studied and amplified from the RNA of Penicillium sp. Y-21 by RT-PCR. The results showed that the pel gene played an important role in enzyme production. Afterwards, an enzyme cocktail can be added to chicken feed as an additive, which improves animal growth and feed efficiency.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Response surface method to optimize the production and characterization of lipase from Penicillium verrucosum in solid-state fermentation.Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2008 Feb;31(2):119-25. doi: 10.1007/s00449-007-0154-8. Epub 2007 Aug 11. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2008. PMID: 17694331
-
Lipase production by Penicillium restrictum using solid waste of industrial babassu oil production as substrate.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2000 Spring;84-86:1137-45. doi: 10.1385/abab:84-86:1-9:1137. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2000. PMID: 10849864
-
Lipase production by solid-state fermentation: cultivation conditions and operation of tray and packed-bed bioreactors.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2005 Spring;121-124:105-16. doi: 10.1385/abab:121:1-3:0105. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2005. PMID: 15917592
-
Enhancement of Penicillium echinulatum glycoside hydrolase enzyme complex.J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016 May;43(5):627-39. doi: 10.1007/s10295-016-1746-6. Epub 2016 Feb 27. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 26922416
-
Transcription Factor Atf1 Regulates Expression of Cellulase and Xylanase Genes during Solid-State Fermentation of Ascomycetes.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019 Nov 27;85(24):e01226-19. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01226-19. Print 2019 Dec 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31604764 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nwuche CO, Ogbonna JC. Isolation of lipase producing fungi from palm oil Mill effluent (POME) dump sites at Nsukka. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2011;54(1):113–116. doi: 10.1590/S1516-89132011000100015. - DOI
-
- Cai ZQ, et al. Biosynthesis of myristyl serinate by immobilized Candida antarcticalipase in two-phase system. J. Mol. Catal. B-Enzym. 2014;108:118–122. doi: 10.1016/j.molcatb.2014.07.008. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

