The effect of the Er,Cr:YSGG laser combined casein phosphopeptide amorphous calcium phosphate for enamel remineralisation: a systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro studies
- PMID: 37667086
- PMCID: PMC10477104
- DOI: 10.1007/s10103-023-03864-5
The effect of the Er,Cr:YSGG laser combined casein phosphopeptide amorphous calcium phosphate for enamel remineralisation: a systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro studies
Abstract
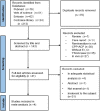
The purpose of this systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro studies was to evaluate the effect of the 2780 nm Er,Cr:YSGG laser combined with casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate (CPP-ACP) for enamel remineralisation. The electronic PubMed, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, and EMBASE databases were searched, with no language or date restrictions, up to January 2023. Two reviewers independently performed research information extraction and quality assessment. Continuous variables were analysed by standard mean difference (SMD) with a 95% confidence interval (CI). The statistical analyses were conducted using Review Manager (Version 5.4; Rev Man) and Cochrane Collaboration (2020). Finally, four trials were included for meta-analysis. According to the comprehensive results, the effect of the Er,Cr:YSGG laser combined with CPP-ACP on enamel remineralisation was significantly better than that of CPP-ACP alone: surface microhardness (SMD = - 1.83, 95% CI: [- 2.98, - 0.69], P = 0.002); lesion depth (SMD = 6.63, 95% CI: [4.98, 8.28], P < 0.001). Under the limitations of this meta-analysis, the results show that the Er,Cr:YSGG laser combined with CPP-ACP has a better effect on enamel remineralisation than CPP-ACP alone. The combination of the Er,Cr:YSGG laser and CPP-ACP may be a feasible method to prevent and treat enamel demineralisation.
Keywords: Casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate; Er,Cr:YSGG laser; Meta-analysis; Remineralisation.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Long term remineralizing effect of casein phosphopeptide amorphous calcium phosphate in white spot lesions: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Technol Health Care. 2024;32(3):1239-1254. doi: 10.3233/THC-230722. Technol Health Care. 2024. PMID: 37599550
-
Effect of laser applications with different agents on dentin surface roughness, bacterial adhesion and tubule occlusion.Clin Oral Investig. 2025 Jun 25;29(7):353. doi: 10.1007/s00784-025-06443-w. Clin Oral Investig. 2025. PMID: 40560267 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of therapies of white spot lesions: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.BMC Oral Health. 2023 Jun 1;23(1):346. doi: 10.1186/s12903-023-03076-x. BMC Oral Health. 2023. PMID: 37264364 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Er: YAG, Er,Cr: YSGG, and Nd: YAG laser irradiation and adhesive systems on the immediate and long-term bond strength of dentin: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Lasers Med Sci. 2023 Jan 3;38(1):32. doi: 10.1007/s10103-022-03699-6. Lasers Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 36595096
-
The effect of bioactive glasses on enamel remineralization: A systematic review.J Dent. 2017 Dec;67:9-17. doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2017.09.007. Epub 2017 Sep 20. J Dent. 2017. PMID: 28939485
Cited by
-
Cariostatic Agents: From Silver Diamine Fluoride to Emerging Bioactive Compounds.Clin Cosmet Investig Dent. 2025 Jun 3;17:237-257. doi: 10.2147/CCIDE.S502433. eCollection 2025. Clin Cosmet Investig Dent. 2025. PMID: 40487005 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kugel G, Arsenault P, Papas A. Treatment modalities for caries management, including a new resin infiltration system. Compend Contin Educ Dent. 2009;3:1–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

