The YAP-TEAD complex promotes senescent cell survival by lowering endoplasmic reticulum stress
- PMID: 37667102
- PMCID: PMC11369890
- DOI: 10.1038/s43587-023-00480-4
The YAP-TEAD complex promotes senescent cell survival by lowering endoplasmic reticulum stress
Abstract
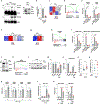
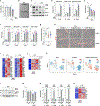
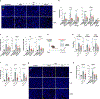
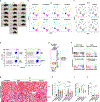
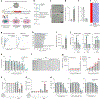
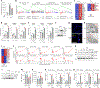
Sublethal cell damage can trigger senescence, a complex adaptive program characterized by growth arrest, resistance to apoptosis and a senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP). Here, a whole-genome CRISPR knockout screen revealed that proteins in the YAP-TEAD pathway influenced senescent cell viability. Accordingly, treating senescent cells with a drug that inhibited this pathway, verteporfin (VPF), selectively triggered apoptotic cell death largely by derepressing DDIT4, which in turn inhibited mTOR. Reducing mTOR function in senescent cells diminished endoplasmic reticulum (ER) biogenesis, triggering ER stress and apoptosis due to high demands on ER function by the SASP. Importantly, VPF treatment decreased the numbers of senescent cells in the organs of old mice and mice exhibiting doxorubicin-induced senescence. Moreover, VPF treatment reduced immune cell infiltration and pro-fibrotic transforming growth factor-β signaling in aging mouse lungs, improving tissue homeostasis. We present an alternative senolytic strategy that eliminates senescent cells by hindering ER activity required for SASP production.
© 2023. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Comment in
-
Leveraging the secretory machinery to eliminate senescent cells.Nat Aging. 2023 Oct;3(10):1183-1184. doi: 10.1038/s43587-023-00500-3. Nat Aging. 2023. PMID: 37709908 No abstract available.
References
-
- Gorgoulis V et al. Cellular senescence: defining a path forward. Cell 179, 813–827 (2019). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

