Correlation between serum soluble ASGR1 concentration and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels: a cross-sectional study
- PMID: 37667265
- PMCID: PMC10476293
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-023-01910-3
Correlation between serum soluble ASGR1 concentration and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
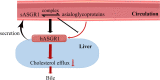
Background: Recent studies have shown that loss-of-function mutations in hepatic asialoglycoprotein receptor 1 (ASGR1) are associated with low levels of circulating cholesterol and a reduced risk of coronary artery disease (CAD). In contrast to ASGR1 on the hepatocyte membrane, serum soluble ASGR1 (sASGR1) is a secreted form that has been detected in circulation. However, the functions of serum sASGR1 are unclear. This study aims to investigate the relationship between human serum sASGR1 concentration and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels.
Methods: In a cohort of 134 participants who underwent coronary angiography examination, basic information was recorded, and blood samples were collected for biochemical testing. The serum sASGR1 concentration was determined by ELISA kits. The relationship between sASGR1 concentration and LDL-C levels was examined using linear regression models and interaction tests. Univariate and multivariate analyses were used to identify clinical variables that affect sASGR1 levels.
Results: After adjusting for potential confounders such as age, sex, BMI, and statin use, the serum sASGR1 concentration was positively correlated with LDL-C levels (β = 0.093, 95% CI: 0.04 to 0.14, P < 0.001). Subgroup analysis and interaction tests showed that the effect of serum sASGR1 concentration on LDL-C levels was significantly influenced by hypertension status (P for interaction = 0.0067). The results of a multivariate linear regression analysis incorporating age, serum TG, LDL-C, nonesterified fatty acid (NEFA), white blood cell counts (WBCC), and fibrinogen revealed that LDL-C (β = 1.005, 95% CI: 0.35 to 1.66, P = 0.003) and WBCC (β = 0.787, 95% CI: 0.41 to 1.16, P < 0.0001) were independent influencing factors for serum sASGR1 levels.
Conclusions: The serum sASGR1 concentration was positively correlated with LDL-C levels. In addition, hypertension status significantly affected the effect of serum sASGR1 on LDL-C levels. This study provides some research ideas for clinical doctors and researchers, as well as some references for additional research on serum sASGR1.
Keywords: ASGR1; Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease; Cholesterol metabolism; Lipid metabolism; Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Ference BA, Ginsberg HN, Graham I, Ray KK, Packard CJ, Bruckert E, et al. Low-density lipoproteins cause atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. 1. Evidence from genetic, epidemiologic, and clinical studies. A consensus statement from the European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel. Eur Heart J. 2017;38(32):2459–72. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehx144. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study Group. Randomised trial of cholesterol lowering in 4444 patients with coronary heart disease: the Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study (4S). Lancet. 1994;344(8934):1383–9. - PubMed
-
- Long-Term Intervention with Pravastatin in Ischaemic Disease (LIPID) Study Group. Prevention of cardiovascular events and death with pravastatin in patients with coronary heart disease and a broad range of initial cholesterol levels. N Engl J Med. 1998;339(19):1349–57. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2022JJ40675/Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2021JJ40852/Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China
- 8220187/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82100495/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- B202305037231/Scientific Research Project of Hunan Provincial Health Commission
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

