Non-Clinical Toxicology Evaluation of the Novel Non-ATP Competitive Oral PI3 Kinase Delta Inhibitor Roginolisib
- PMID: 37667445
- PMCID: PMC10629260
- DOI: 10.1177/10915818231200419
Non-Clinical Toxicology Evaluation of the Novel Non-ATP Competitive Oral PI3 Kinase Delta Inhibitor Roginolisib
Abstract
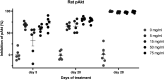
Roginolisib (IOA-244) is a novel, non-ATP competitive phosphoinositide-3-kinase (PI3K) delta inhibitor that regulates Akt/mTOR signaling. Roginolisib was administered once daily to rats and dogs in dose-range finding (DRF) and 4-week GLP toxicology studies. Free plasma levels of roginolisib exceeded the cellular target engagement IC90 for PI3Kδ for ≥12 hours at doses of 5 mg/kg, the IC90 for PI3Kβ for ≥2 hours at doses ≥15 mg/kg, and the IC50 for PI3Kα for ≥2 hours at dose levels ≥45 mg/kg. Toxicity in rats occurred at doses ≥100 mg/kg. In dogs, we observed dose-dependent skin and gastrointestinal toxicity and doses ≥30 mg/kg had a greater incidence of mortality. Lymphoid tissue toxicity occurred in both species. Toxicities in dogs observed at the ≥15 mg/kg dose, affecting the digestive mucosa, liver, and skin, cleared after treatment cessation. Doses ≤75 mg/kg were tolerated in rats and the no-observed-adverse-effect-level (NOAEL) in rats was 15 mg/kg. Due to mainly epithelial lesions of the skin at 5 mg/kg and necrotizing damage of the intestinal epithelia at ≥15 mg/kg, no NOAEL was determined in dogs. However, the adverse effects observed in dogs at 5 mg/kg were considered monitorable and reversible in patients with advanced malignancies. Furthermore, the PK profile subsequently proved to be a decisive factor for achieving selective PI3Kδ inhibition without the toxicities observed in dogs. As the result of the unique PK profile of roginolisib, patients were able to take daily roginolisib without dose modification and showed pharmacodynamic PI3Kδ inhibition over several months without gastrointestinal or dermatologic toxicities.
Keywords: PI3Kδ; phosphoinositide-3 kinase delta; phosphoinositide-3 kinase inhibitors; roginolisib; toxicology.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interestsThe author(s) declared the following potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: Marcel Deken, Michael Lahn, and Lars van der Veen are employees of iOnctura. Michael Schmitt is an employee of Merck Healthcare.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The highly selective and oral phosphoinositide 3-kinase delta (PI3K-δ) inhibitor roginolisib induces apoptosis in mesothelioma cells and increases immune effector cell composition.Transl Oncol. 2024 May;43:101857. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2023.101857. Epub 2024 Feb 27. Transl Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38412661 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative systems pharmacology model-based investigation of adverse gastrointestinal events associated with prolonged treatment with PI3-kinase inhibitors.CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2022 May;11(5):616-627. doi: 10.1002/psp4.12749. Epub 2021 Dec 13. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34850607 Free PMC article.
-
Absorption, Distribution, and Binding Profile of ME-401, a Potent and Selective Oral Small-Molecule Inhibitor of Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase δ (PI3Kδ) in Animal and B-Cell Lymphoma Models.Target Oncol. 2019 Oct;14(5):603-611. doi: 10.1007/s11523-019-00668-y. Target Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31506873 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic and toxicological considerations for phosphoinositide 3-kinase delta inhibitors in the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2023 Sep;19(9):617-633. doi: 10.1080/17425255.2023.2260305. Epub 2023 Sep 15. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 37714711 Review.
-
New inhibitors of the PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway: insights into mTOR signaling from a new generation of Tor Kinase Domain Inhibitors (TORKinibs).Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2010;347:241-62. doi: 10.1007/82_2010_64. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20549474 Review.
References
-
- Boller D, Schramm A, Doepfner KT, et al. Targeting the phosphoinositide 3-kinase isoform p110delta impairs growth and survival in neuroblastoma cells. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14(4):1172-1181. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

