Three-dimensional echo-shifted EPI with simultaneous blip-up and blip-down acquisitions for correcting geometric distortion
- PMID: 37667533
- PMCID: PMC10903279
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.29828
Three-dimensional echo-shifted EPI with simultaneous blip-up and blip-down acquisitions for correcting geometric distortion
Abstract
Purpose: EPI with blip-up/down acquisition (BUDA) can provide high-quality images with minimal distortions by using two readout trains with opposing phase-encoding gradients. Because of the need for two separate acquisitions, BUDA doubles the scan time and degrades the temporal resolution when compared to single-shot EPI, presenting a major challenge for many applications, particularly fMRI. This study aims at overcoming this challenge by developing an echo-shifted EPI BUDA (esEPI-BUDA) technique to acquire both blip-up and blip-down datasets in a single shot.
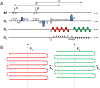
Methods: A 3D esEPI-BUDA pulse sequence was designed by using an echo-shifting strategy to produce two EPI readout trains. These readout trains produced a pair of k-space datasets whose k-space trajectories were interleaved with opposite phase-encoding gradient directions. The two k-space datasets were separately reconstructed using a 3D SENSE algorithm, from which time-resolved B0 -field maps were derived using TOPUP in FSL and then input into a forward model of joint parallel imaging reconstruction to correct for geometric distortion. In addition, Hankel structured low-rank constraint was incorporated into the reconstruction framework to improve image quality by mitigating the phase errors between the two interleaved k-space datasets.
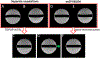
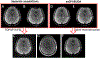
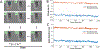
Results: The 3D esEPI-BUDA technique was demonstrated in a phantom and an fMRI study on healthy human subjects. Geometric distortions were effectively corrected in both phantom and human brain images. In the fMRI study, the visual activation volumes and their BOLD responses were comparable to those from conventional 3D echo-planar images.
Conclusion: The improved imaging efficiency and dynamic distortion correction capability afforded by 3D esEPI-BUDA are expected to benefit many EPI applications.
Keywords: 3D EPI; Echo shifting; Hankel low-rank reconstruction; blip-up and blip-down acquisitions (BUDA); fMRI; geometric distortion correction.
© 2023 The Authors. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Figures



Similar articles
-
3D-EPI blip-up/down acquisition (BUDA) with CAIPI and joint Hankel structured low-rank reconstruction for rapid distortion-free high-resolution mapping.Magn Reson Med. 2023 May;89(5):1961-1974. doi: 10.1002/mrm.29578. Epub 2023 Jan 27. Magn Reson Med. 2023. PMID: 36705076 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced distortion artifact whole brain CBF mapping using blip-reversed non-segmented 3D echo planar imaging with pseudo-continuous arterial spin labeling.Magn Reson Imaging. 2017 Dec;44:119-124. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2017.08.011. Epub 2017 Sep 1. Magn Reson Imaging. 2017. PMID: 28867670 Free PMC article.
-
Distortion-free, high-isotropic-resolution diffusion MRI with gSlider BUDA-EPI and multicoil dynamic B0 shimming.Magn Reson Med. 2021 Aug;86(2):791-803. doi: 10.1002/mrm.28748. Epub 2021 Mar 10. Magn Reson Med. 2021. PMID: 33748985 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient T2 mapping with blip-up/down EPI and gSlider-SMS (T2 -BUDA-gSlider).Magn Reson Med. 2021 Oct;86(4):2064-2075. doi: 10.1002/mrm.28872. Epub 2021 May 28. Magn Reson Med. 2021. PMID: 34046924 Free PMC article.
-
Minimizing magnetic resonance image geometric distortion at 7 Tesla for frameless presurgical planning using skin-adhered fiducials.Med Phys. 2023 Feb;50(2):694-701. doi: 10.1002/mp.16035. Epub 2022 Nov 12. Med Phys. 2023. PMID: 36301228 Review.
Cited by
-
Steady-state free precession for T2* relaxometry: All echoes in every readout with k-space aliasing.Magn Reson Med. 2025 Oct;94(4):1563-1576. doi: 10.1002/mrm.30590. Epub 2025 Jun 2. Magn Reson Med. 2025. PMID: 40457600 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bernstein MA, King KF, Zhou XJ. Handbook of MRI pulse sequences. In: Amsterdam: Elsevier, Academic Press. ; 2004.
-
- Rohde GK, Barnett AS, Basser PJ, Marenco S, Pierpaoli C. Comprehensive approach for correction of motion and distortion in diffusion-weighted MRI. Magn Reson Med. 2004;51(1):103–114. - PubMed
-
- Zhou XJ, Du YP, Bernstein MA, Reynolds HG, Maier JK, Polzin JA. Concomitant magnetic-field-induced artifacts in axial echo planar imaging. Magn Reson Med. 1998;39(4):596–605. - PubMed
-
- Jezzard P. Correction of geometric distortion in fMRI data. Neuroimage. 2012;62:648–651. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

