Risk factors of foot ulcers in patients with end-stage renal disease on dialysis: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 37667546
- PMCID: PMC10782048
- DOI: 10.1111/iwj.14348
Risk factors of foot ulcers in patients with end-stage renal disease on dialysis: A meta-analysis
Retraction in
-
RETRACTION: Risk Factors of Foot Ulcers in Patients With End-Stage Renal Disease on Dialysis: A Meta-Analysis.Int Wound J. 2025 Mar;22(3):e70316. doi: 10.1111/iwj.70316. Int Wound J. 2025. PMID: 40049754 Free PMC article.
Abstract
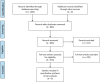
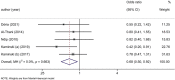
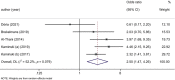
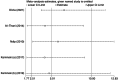
The present study aims to assess the risk factors for foot ulcers in patients undergoing dialysis for end-stage renal disease (ESRD) and to provide evidence-based guidance for prevention and treatment. A systematic search was conducted on PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, China National Knowledge Infrastructure, Chinese Biomedical Literature Database and Wanfang Data from the database inception until May 2023 to identify relevant studies investigating the risk factors for foot ulcers in dialysis patients with ESRD. Two independent researchers conducted the literature screening and data extraction. The meta-analysis was performed using STATA 17.0 software. Ultimately, six articles comprising 1620 patients were included for analysis. The meta-analysis revealed that male (OR, 1.464; 95% CI: 1.082-1.980, p = 0.013), hypertension (OR, 1.781; 95% CI: 1.293-2.4550, p < 0.001), peripheral artery disease (PAD) (OR, 5.014; 95% CI: 2.514-9.998, p < 0.001), type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) (OR, 2.993; 95% CI: 1.477-6.065, p = 0.002) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) (OR, 2.498; 95% CI:1.466-4.256, p = 0.001) were risk factors for foot ulcers in dialysis patients with ESRD. Conversely, the female sex (OR, 0.683; 95% CI: 0.505-0.924, p = 0.013) was a protective factor against foot ulcers. Our analysis revealed that male sex, hypertension, PAD, T1DM and T2DM were risk factors for foot ulcers in patients undergoing dialysis for ESRD. Conversely, the female sex was a protective factor against foot ulcers. Therefore, it is crucial to strengthen health education that targets patients with these risk factors and regularly screen high-risk individuals. Early detection and treatment can help delay disease progression.
Keywords: dialysis; end-stage renal disease; foot ulcers; meta-analysis; risk factors.
© 2023 The Authors. International Wound Journal published by Medicalhelplines.com Inc and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Prevention of foot ulcers in patients with diabetes and end stage renal disease.Nephrol Nurs J. 2003 Feb;30(1):39-43. Nephrol Nurs J. 2003. PMID: 12674948 Clinical Trial.
-
Reconstructive vascular surgery and the extent of tissue damage due to diabetic foot ulcers relates to risk of new ulceration in patients with PAD.J Wound Care. 2015 Dec;24(12):590, 592-7. doi: 10.12968/jowc.2015.24.12.590. J Wound Care. 2015. PMID: 26654740
-
Micro- and macrovascular complications and risk factors for foot ulceration and amputation in individuals receiving dialysis with and without diabetes.Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2022 Jan;5(1):e00305. doi: 10.1002/edm2.305. Epub 2021 Oct 17. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2022. PMID: 34658171 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetic foot disease in people with advanced nephropathy and those on renal dialysis.Curr Diab Rep. 2010 Aug;10(4):283-90. doi: 10.1007/s11892-010-0128-0. Curr Diab Rep. 2010. PMID: 20532700 Review.
-
Influencing factors for the recurrence of diabetic foot ulcers: A meta-analysis.Int Wound J. 2023 May;20(5):1762-1775. doi: 10.1111/iwj.14017. Epub 2022 Nov 17. Int Wound J. 2023. PMID: 36385501 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
RETRACTION: Risk Factors of Foot Ulcers in Patients With End-Stage Renal Disease on Dialysis: A Meta-Analysis.Int Wound J. 2025 Mar;22(3):e70316. doi: 10.1111/iwj.70316. Int Wound J. 2025. PMID: 40049754 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arhuidese I, Nejim B, Aji EA, Canner J, Malas MB. Survival after major lower extremity amputation in patients with end‐stage renal disease. J Vasc Surg. 2019;70(4):1291‐1298. - PubMed
-
- Zhang L, Wang F, Wang L, et al. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in China: a cross‐sectional survey. Lancet. 2012;379(9818):815‐822. - PubMed
-
- Schaper NC, Van Netten JJ, Apelqvist J, Lipsky BA, Bakker K. Prevention and management of foot problems in diabetes: a summary guidance for daily practice 2015, based on the IWGDF guidance documents. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2017;124:84‐92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

