Serum Metabolomics Analysis of Skin-Involved Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Association of Anti-SSA Antibodies with Photosensitivity
- PMID: 37667802
- PMCID: PMC10475307
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S426337
Serum Metabolomics Analysis of Skin-Involved Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Association of Anti-SSA Antibodies with Photosensitivity
Abstract
Purpose: Systemic lupus erythematosus is a heterogeneous autoimmune disease in which skin involvement is a common manifestation. It is currently thought that the photosensitivity of SLE skin involvement is associated with anti-SSA antibodies. This study aimed to expand the current state of knowledge surrounding the molecular pathophysiology of SLE skin photosensitivity through Serum metabolomics analysis.
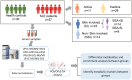
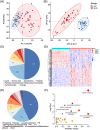
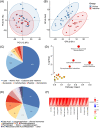
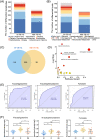
Patients and methods: The serum metabolites of 23 cases of skin-involved SLE (SI) group, 14 cases of no SI (NSI) group, and 30 cases of healthy controls (HC) were analyzed by using UPLC-MS/MS technology, and subgroup analysis was performed according to the expression of anti-SSA antibodies in SI. MetaboAnalyst 5.0 was used for enrichment analysis and ROC curve construction, identifying serum metabolic markers of skin-involved SLE associated with anti-SSA antibodies.
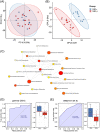
Results: We identified several metabolites and metabolic pathways associated with SLE photosensitivity. Two metabolites, SM (d18:1/24:0) and gamma-CEHC can distinguish between anti-SSA antibody-positive and negative SI, with AUC of 0.829 and 0.806. These two photosensitization-related substances may be potential markers of skin involvement in SLE associated with anti-SSA antibody.
Conclusion: This study provides new insights into the pathogenesis of SI patients, and provides a new molecular biological basis for the association between anti-SSA antibodies and skin photoallergic manifestations of SLE.
Keywords: anti-SSA antibodies; biomarkers; metabolomics; photosensitivity; systemic lupus erythematosus.
© 2023 Lu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

