Gut microbiota from patients with COVID-19 cause alterations in mice that resemble post-COVID symptoms
- PMID: 37668317
- PMCID: PMC10481883
- DOI: 10.1080/19490976.2023.2249146
Gut microbiota from patients with COVID-19 cause alterations in mice that resemble post-COVID symptoms
Abstract
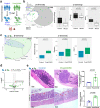
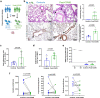
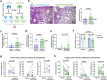
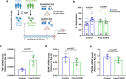
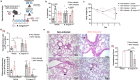
Long-term sequelae of coronavirus disease (COVID)-19 are frequent and of major concern. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection affects the host gut microbiota, which is linked to disease severity in patients with COVID-19. Here, we report that the gut microbiota of post-COVID subjects had a remarkable predominance of Enterobacteriaceae strains with an antibiotic-resistant phenotype compared to healthy controls. Additionally, short-chain fatty acid (SCFA) levels were reduced in feces. Fecal transplantation from post-COVID subjects to germ-free mice led to lung inflammation and worse outcomes during pulmonary infection by multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. transplanted mice also exhibited poor cognitive performance. Overall, we show prolonged impacts of SARS-CoV-2 infection on the gut microbiota that persist after subjects have cleared the virus. Together, these data demonstrate that the gut microbiota can directly contribute to post-COVID sequelae, suggesting that it may be a potential therapeutic target.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; antimicrobial-resistance; inflammation; microbiota; post-COVID.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization . COVID-19 weekly epidemiological update, 16 March 2023. 134th ed. 2023. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/366534.
-
- Augustin M, Schommers P, Stecher M, Dewald F, Gieselmann L, Gruell H, Horn C, Vanshylla K, Di Cristanziano V, Osebold L.. Post-COVID syndrome in non-hospitalised patients with COVID-19: a longitudinal prospective cohort study. Lancet Reg Heal. 2021;6:100122. doi:10.1016/j.lanepe.2021.100122. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
