World-first report of low anterior resection for rectal cancer with the hinotori™ Surgical Robot System: a case report
- PMID: 37668746
- PMCID: PMC10480373
- DOI: 10.1186/s40792-023-01705-9
World-first report of low anterior resection for rectal cancer with the hinotori™ Surgical Robot System: a case report
Abstract
Background: The hinotori™ Surgical Robot System was approved for use in colorectal cancer surgery in Japan in 2022. This robot has advantages, such as an operation arm with eight axes, an adjustable arm base, and a flexible three-dimensional viewer, and is expected to be utilized in rectal cancer surgery. Herein, we report the world's first surgery for rectal cancer using the hinotori™ Surgical Robot System.
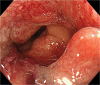
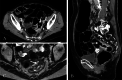
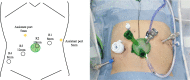
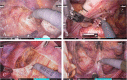
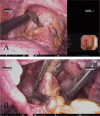
Case presentation: A 71-year-old woman presented to our hospital with bloody stools. A colonoscopy revealed type 2 advanced cancer in the rectum, and a histological examination exposed a well-differentiated adenocarcinoma. Abdominal enhanced computed tomography divulged rectal wall thickening without significant swelling of the lymph nodes or distant metastasis. Pelvic magnetic resonance imaging showed tumor invasion beyond the intrinsic rectal muscle layer. The patient was diagnosed with cStage IIa (cT3N0M0) rectal cancer and underwent low anterior resection using the hinotori™ Surgical Robot System. Based on an adequate simulation, surgery was safely performed with appropriate port placement and arm base-angle adjustment. The operating time was 262 min, with a cockpit time of 134 min. Subsequently, the patient was discharged 10 days postoperatively without complications. The pathological diagnosis was pStage IIA (cT3N0M0) and the circumferential resection margin was 6 mm.
Conclusions: We report the first case of low anterior resection for rectal cancer using the hinotori™ Surgical Robot System, in which a safe and appropriate oncological surgery was performed.
Keywords: Hinotori; Low anterior resection; Rectal cancer; Robotic surgery.
© 2023. Japan Surgical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The following authors have no financial disclosures: RM, KO, EA, MM, AN, MI, MI, TK, MT, TI, TO, AK, and IT.
Figures

References
-
- Jayne D, Pigazzi A, Marshall H, Croft J, Corrigan N, Copeland J, et al. Effect of robotic-assisted vs conventional laparoscopic surgery on risk of conversion to open laparotomy among patients undergoing resection for rectal cancer: the ROLARR randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2017;318:1569–1580. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.7219. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Matsuyama T, Endo H, Yamamoto H, Takemasa I, Uehara K, Hanai T, et al. Outcomes of robot-assisted versus conventional laparoscopic low anterior resection in patients with rectal cancer: propensity-matched analysis of the National Clinical Database in Japan. BJS Open. 2021 doi: 10.1093/bjsopen/zrab083. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

