Chitosan oligosaccharide suppresses osteosarcoma malignancy by inhibiting CEMIP via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway
- PMID: 37668818
- PMCID: PMC10480286
- DOI: 10.1007/s12032-023-02165-9
Chitosan oligosaccharide suppresses osteosarcoma malignancy by inhibiting CEMIP via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway
Abstract
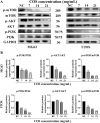
Osteosarcoma is a malignant bone tumor that is prone to metastasize early and primarily affects children and adolescents. Cell migration-inducing protein (CEMIP) plays a crucial role in the progression and malignancy of various tumor diseases, including osteosarcoma. Chitosan oligosaccharide (COS), an oligomer isolated from chitin, has been found to have significant anti-tumor activity in various cancers. This study investigates the effects of COS on CEMIP expression in osteosarcoma and explores the underlying mechanism. In present study, in vitro experiments were conducted to confirm the inhibitory activity of COS on human osteosarcoma cells. Our results demonstrate that COS possesses inhibitory effects against human osteosarcoma cells and significantly suppresses CEMIP expression in vitro. Next, we studied the inhibition of the expression of CEMIP by COS and then performed bioinformatics analysis to explore the potential inhibitory mechanism of COS against signaling pathways involved in regulating CEMIP expression. Bioinformatics analysis predicted a close association between the PI3K signaling pathway and CEMIP expression and that the inhibitory effect of COS on CEMIP expression may be related to PI3K signaling pathway regulation. The results of this study show that COS treatment significantly inhibits CEMIP expression and the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway, as observed both in vitro and in vivo. This study demonstrates that COS could inhibit the expression of CEMIP, which is closely related to osteosarcoma malignancy. This inhibitory effect may be attributed to the inhibition of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in vitro and in vivo.
Keywords: CEMIP; Chitosan oligosaccharide; Osteosarcoma; PI3K; Pathway.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures






Similar articles
-
AIM2 inhibits the proliferation, invasion and migration, and promotes the apoptosis of osteosarcoma cells by inactivating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2022 Feb;25(2):53. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12569. Epub 2021 Dec 16. Mol Med Rep. 2022. PMID: 34913077 Free PMC article.
-
Chitooligosaccharides inhibit tumor progression and induce autophagy through the activation of the p53/mTOR pathway in osteosarcoma.Carbohydr Polym. 2021 Apr 15;258:117596. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117596. Epub 2021 Jan 21. Carbohydr Polym. 2021. PMID: 33593530
-
Calycosin, a Phytoestrogen Isoflavone, Induces Apoptosis of Estrogen Receptor-Positive MG-63 Osteosarcoma Cells via the Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase (PI3K)/AKT/Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) Pathway.Med Sci Monit. 2018 Sep 5;24:6178-6186. doi: 10.12659/MSM.910201. Med Sci Monit. 2018. PMID: 30182951 Free PMC article.
-
To Investigate the Occurrence and Development of Colorectal Cancer Based on the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023 Feb 24;28(2):37. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2802037. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023. PMID: 36866550 Review.
-
The role of CEMIP in cancers and its transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation.PeerJ. 2024 Feb 19;12:e16930. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16930. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38390387 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Elucidating Ras protein as a dual therapeutic target for inflammation and cancer: a review.Discov Oncol. 2025 Jun 7;16(1):1029. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02783-x. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40483365 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chitosan oligosaccharide enhances the anti-cancer effects of 5-fluorouracil on SNU-C5 colorectal cancer cells by activating ERK.Oncol Res. 2025 Mar 19;33(4):873-884. doi: 10.32604/or.2024.052003. eCollection 2025. Oncol Res. 2025. PMID: 40191714 Free PMC article.
References
-
- He J, Zhang W, Di T, Meng J, Qi Y, Li G, Zhang Y, Su H, Yan W. Water extract of sporoderm-broken spores of Ganoderma lucidum enhanced pd-l1 antibody efficiency through downregulation and relieved complications of pd-l1 monoclonal antibody. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;131:110541. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110541. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

