Cognitive-Based Interventions for Improving Psychological Health and Well-Being for Parents of Children with Developmental Disabilities: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- PMID: 37668850
- PMCID: PMC11362495
- DOI: 10.1007/s10803-023-06063-x
Cognitive-Based Interventions for Improving Psychological Health and Well-Being for Parents of Children with Developmental Disabilities: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Abstract
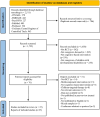
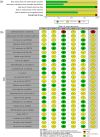
This review aims to systematically summarize existing evidence to determine the effectiveness of cognitive-based interventions (CBIs) on psychological health and well-being among parents of children with developmental disabilities (DD). Six databases were searched to identify eligible randomized controlled trials (RCTs) from their inception to April 2023. The revised Cochrane Risk of Bias tool for RCTs was applied to assess the risk of bias and the certainty of evidence was evaluated using the Grading of Recommendation, Assessment, Development and Evaluation. Meta-analyses were conducted using a random-effects model. Twenty-five RCTs involving 1915 participants were identified. The results indicated that CBIs reduced parental stress levels (Hedges' g = - 0.69), depressive symptoms (g = - 0.95), anxiety levels (g = - 0.78), and parental distress (g = - 0.29), and improved parental well-being (g = 0.62) and parent‒child relationships (g = 0.43) postintervention compared with the active/inactive control groups. Subgroup analysis of the effectiveness of interventions using mindfulness-based interventions and cognitive behavioural therapy showed positive effects. The favourable intervention duration and participant targets were also identified in this review. Furthermore, the effects of CBIs were impacted by the different types of DD among the children. This review highlighted the positive effects of CBIs on parental stress levels, depressive symptoms, anxiety levels, parental distress levels, parental well-being levels, and parent‒child relationships. Future well-designed RCTs are needed to further investigate the effects of MBIs and CBT interventions on children with DD and their parents, as well as the factors and mechanisms of action affecting the efficacy of these interventions.
Keywords: Cognitive behavioural therapy; Developmental disabilities; Meta-analysis; Mindfulness; Parents.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest between all authors.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Effectiveness of Mindfulness-Based Interventions in Improving the Mental Health of Parents of Children with Intellectual or Developmental Disabilities: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Autism Dev Disord. 2025 Mar 13. doi: 10.1007/s10803-025-06790-3. Online ahead of print. J Autism Dev Disord. 2025. PMID: 40080346
-
Psychological interventions in reducing stress, depression and anxiety among parents of children and adolescents with developmental disabilities: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Adv Nurs. 2019 Dec;75(12):3316-3330. doi: 10.1111/jan.14166. Epub 2019 Aug 27. J Adv Nurs. 2019. PMID: 31359461
-
The effects of mindfulness-based interventions on symptoms of depression, anxiety, and cancer-related fatigue in oncology patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2022 Jul 14;17(7):e0269519. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0269519. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35834503 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Mindfulness-Based and Acceptance Commitment Therapy-Based Interventions to Improve the Mental Well-Being Among Parents of Children with Developmental Disabilities: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Autism Dev Disord. 2022 Jun;52(6):2770-2783. doi: 10.1007/s10803-021-04893-1. Epub 2021 Jun 28. J Autism Dev Disord. 2022. PMID: 34181139 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of information technology-based cognitive behavioral therapy on depression and anxiety symptoms among older adults: Systematic review and meta-analysis.Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2025 Mar-Apr;93:9-19. doi: 10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2024.12.022. Epub 2024 Dec 25. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 39761612
Cited by
-
The effectiveness of Acceptance and Commitment Therapy on parental stress in parents of special children: a meta-analysis.Child Adolesc Psychiatry Ment Health. 2025 Jul 21;19(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s13034-025-00944-y. Child Adolesc Psychiatry Ment Health. 2025. PMID: 40691592 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effectiveness of Mindfulness-Based Interventions in Improving the Mental Health of Parents of Children with Intellectual or Developmental Disabilities: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Autism Dev Disord. 2025 Mar 13. doi: 10.1007/s10803-025-06790-3. Online ahead of print. J Autism Dev Disord. 2025. PMID: 40080346
-
The Roles of Parental Psychological Flexibility, Mindfulness, and Self-Compassion in Affecting Mental Health and Self-Efficacy in Parents of Children With or Without Hearing Loss: An Analysis of the Parallel Mediation Model.Nurs Open. 2025 Apr;12(4):e70180. doi: 10.1002/nop2.70180. Nurs Open. 2025. PMID: 40186878 Free PMC article.
-
Being a parent of children with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder.Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992). 2025 Mar 17;71(1):e20241335. doi: 10.1590/1806-9282.20241335. eCollection 2025. Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992). 2025. PMID: 40105566 Free PMC article.
-
Factors Associated With Depression in Caregivers of Adults With Down Syndrome.J Intellect Disabil Res. 2025 Mar;69(3):234-242. doi: 10.1111/jir.13208. Epub 2024 Dec 24. J Intellect Disabil Res. 2025. PMID: 39717996 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abidin, R. R. (1983). Parenting stress index: Manual, administration booklet, [and] research update.
-
- Abidin, R. R. (1990). Parenting stress index-short form. Pediatric psychology press Charlottesville.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

