Prediction of early neurological deterioration in acute ischemic stroke patients treated with intravenous thrombolysis
- PMID: 37668997
- PMCID: PMC10925869
- DOI: 10.1177/0271678X231200117
Prediction of early neurological deterioration in acute ischemic stroke patients treated with intravenous thrombolysis
Abstract
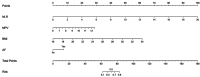
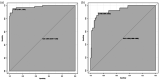
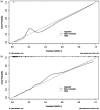
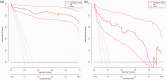
A proportion of acute ischemic stroke (AIS) patients suffer from early neurological deterioration (END) within 24 hours following intravenous thrombolysis (IVT), which greatly increases the risk of poor prognosis of these patients. Therefore, we aimed to explore the predictors of early neurological deterioration of ischemic origin (ENDi) in AIS patients after IVT and develop a nomogram prediction model. This study collected 244 AIS patients with post-thrombolysis ENDi as the derivation cohort and 155 patients as the validation cohort. To establish a nomogram prediction model, risk factors were identified by multivariate logistic regression analysis. The results showed that neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) (OR 2.616, 95% CI 1.640-4.175, P < 0.001), mean platelet volume (MPV) (OR 3.334, 95% CI 1.351-8.299, P = 0.009), body mass index (BMI) (OR 1.979, 95% CI 1.285-3.048, P = 0.002) and atrial fibrillation (AF) (OR 8.012, 95% CI 1.341-47.873, P = 0.023) were significantly associated with ENDi. The area under the curve of the prediction model constructed from the above four factors was 0.981 (95% CI 0.961-1.000) and the calibration curve was close to the ideal diagonal line. Therefore, this nomogram prediction model exhibited good discrimination and calibration power and might be a reliable and easy-to-use tool to predict post-thrombolysis ENDi in AIS patients.
Keywords: Acute ischemic stroke; early neurological deterioration; intravenous thrombolysis; nomogram; prediction model.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nomogram to Predict Symptomatic Intracranial Hemorrhage after Intravenous Thrombolysis in Acute Ischemic Stroke in Asian Population.Curr Neurovasc Res. 2021;18(5):543-551. doi: 10.2174/1567202619666211223150907. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2021. PMID: 34951382
-
Construction of a prediction model for risk of early neurological deterioration following intravenous thrombolysis in patients with acute ischemic stroke.Technol Health Care. 2023;31(6):2213-2223. doi: 10.3233/THC-230140. Technol Health Care. 2023. PMID: 37302055
-
Prediction of Early Neurological Deterioration in Individuals With Minor Stroke and Large Vessel Occlusion Intended for Intravenous Thrombolysis Alone.JAMA Neurol. 2021 Mar 1;78(3):321-328. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2020.4557. JAMA Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33427887 Free PMC article.
-
Circadian Rhythm and Risk of Hemorrhagic Transformation after Acute Ischemic Stroke Treated with Intravenous Thrombolysis - A Systematic Review.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2023;22(10):1493-1506. doi: 10.2174/1871527322666221004113752. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2023. PMID: 36200200
-
Prognostic value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in acute ischemic stroke patients treated with intravenous thrombolysis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Neurol. 2021 May 11;21(1):191. doi: 10.1186/s12883-021-02222-8. BMC Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33975565 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Potential Predictive Value of Platelet Distribution Width for Functional Outcome After Ischemic Stroke.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Apr;62(4):4292-4300. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04556-z. Epub 2024 Oct 23. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 39441329 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a Risk Tracking Model for Neurological Deterioration in Ischemic Stroke Based on Blood Pressure Dynamics.J Am Heart Assoc. 2025 Apr;14(7):e036287. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.124.036287. Epub 2025 Mar 26. J Am Heart Assoc. 2025. PMID: 40135582 Free PMC article.
-
Factors associated with early neurological deterioration after intravenous thrombolysis in acute cerebral infarction patients and establishment of a predictive model.Am J Transl Res. 2025 Jan 15;17(1):247-253. doi: 10.62347/GIIG7402. eCollection 2025. Am J Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 39959213 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive value of the BDH2-MN2 nomogram model for prognosis at 3 months after receiving intravenous thrombolysis in patients with acute ischemic stroke.Arch Med Sci. 2024 May 13;20(4):1143-1152. doi: 10.5114/aoms/176740. eCollection 2024. Arch Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39439681 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning-based prediction of early neurological deterioration after intravenous thrombolysis for stroke: insights from a large multicenter study.Front Neurol. 2024 Sep 9;15:1408457. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1408457. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39314867 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, et al.. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: 2019 update to the 2018 guidelines for the early management of acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2019; 50: e344–e418. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

