Parallel molecular computation on digital data stored in DNA
- PMID: 37669382
- PMCID: PMC10500265
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2217330120
Parallel molecular computation on digital data stored in DNA
Abstract
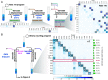
DNA is an incredibly dense storage medium for digital data. However, computing on the stored information is expensive and slow, requiring rounds of sequencing, in silico computation, and DNA synthesis. Prior work on accessing and modifying data using DNA hybridization or enzymatic reactions had limited computation capabilities. Inspired by the computational power of "DNA strand displacement," we augment DNA storage with "in-memory" molecular computation using strand displacement reactions to algorithmically modify data in a parallel manner. We show programs for binary counting and Turing universal cellular automaton Rule 110, the latter of which is, in principle, capable of implementing any computer algorithm. Information is stored in the nicks of DNA, and a secondary sequence-level encoding allows high-throughput sequencing-based readout. We conducted multiple rounds of computation on 4-bit data registers, as well as random access of data (selective access and erasure). We demonstrate that large strand displacement cascades with 244 distinct strand exchanges (sequential and in parallel) can use naturally occurring DNA sequence from M13 bacteriophage without stringent sequence design, which has the potential to improve the scale of computation and decrease cost. Our work merges DNA storage and DNA computing, setting the foundation of entirely molecular algorithms for parallel manipulation of digital information preserved in DNA.
Keywords: DNA computation; DNA storage; molecular programming; strand displacement.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures




References
-
- Church G. M., Gao Y., Kosuri S., Next-generation digital information storage in DNA. Science 337, 1628 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Ceze L., Nivala J., Strauss K., Molecular digital data storage using DNA. Nat. Rev. Genet. 20, 456–466 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Organick L., et al. , Random access in large-scale DNA data storage. Nat. Biotechnol. 36, 242–248 (2018). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

