Design, synthesis, and evaluation of a mitoxantrone probe (MXP) for biological studies
- PMID: 37669721
- PMCID: PMC10528225
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2023.129465
Design, synthesis, and evaluation of a mitoxantrone probe (MXP) for biological studies
Abstract
Mitoxantrone (MX) is a robust chemotherapeutic with well-characterized applications in treating certain leukemias and advanced breast and prostate cancers. The canonical mechanism of action associated with MX is its ability to intercalate DNA and inhibit topoisomerase II, giving it the designation of a topoisomerase II poison. Years after FDA approval, investigations have unveiled novel protein-binding partners, such as methyl-CpG-binding domain protein (MBD2), PIM1 serine/threonine kinase, RAD52, and others that may contribute to the therapeutic profile of MX. Moreover, recent proteomic studies have revealed MX's ability to modulate protein expression, illuminating the complex cellular interactions of MX. Although mechanistically relevant, the differential expression across the proteome does not address the direct interaction with potential binding partners. Identification and characterization of these MX-binding cellular partners will provide the molecular basis for the alternate mechanisms that influence MX's cytotoxicity. Here, we describe the design and synthesis of a MX-biotin probe (MXP) and negative control (MXP-NC) that can be used to define MX's cellular targets and expand our understanding of the proteome-wide profile for MX. In proof of concept studies, we used MXP to successfully isolate a recently identified protein-binding partner of MX, RAD52, in a cell lysate pulldown with streptavidin beads and western blotting.
Keywords: Biotin; DNA repair; Mitoxantrone; Probe; RAD52.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
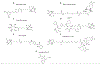


Update of
-
Design, synthesis, and evaluation of a mitoxantrone probe (MXP) for biological studies.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Apr 11:2023.04.11.536471. doi: 10.1101/2023.04.11.536471. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2023 Oct 1;94:129465. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2023.129465. PMID: 37090570 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Meissner F; Geddes-McAlister J; Mann M; Bantscheff M, The emerging role of mass spectrometry-based proteomics in drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2022, 21 (9), 637–654. - PubMed
-
- Oda Y; Owa T; Sato T; Boucher B; Daniels S; Yamanaka H; Shinohara Y; Yokoi A; Kuromitsu J; Nagasu T, Quantitative chemical proteomics for identifying candidate drug targets. Anal Chem 2003, 75 (9), 2159–65. - PubMed
-
- Schirle M; Bantscheff M; Kuster B, Mass spectrometry-based proteomics in preclinical drug discovery. Chem Biol 2012, 19 (1), 72–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

