The Validity and Applicability of the Revised Delirium Rating Scale (DRS-R98) for Delirium Severity Assessment in a Critical Care Setting
- PMID: 37670545
- PMCID: PMC10845842
- DOI: 10.1177/08850666231199986
The Validity and Applicability of the Revised Delirium Rating Scale (DRS-R98) for Delirium Severity Assessment in a Critical Care Setting
Abstract
Background: Delirium is a neuropsychiatric syndrome common in critical illness. Worsening delirium severity is associated with poorer clinical outcomes, yet its assessment remains under-reported with most severity assessment tools not validated for critical care. The DRS-R98 is a widely applied and validated tool. The aim of this project is to report the validation and utility of the DRS-R98 in critical illness.
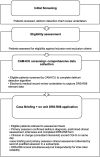
Methods: This prospective, cohort study was conducted in adults with delirium admitted to a critical care unit and predicted to stay for ≥ 24 h. We excluded patients with severe neurological or communication barriers that would have interfered with the DRS-R98 assessment. Patients were screened using a delirium detection algorithm and the Confusion Assessment Method for the Intensive Care Unit. Eligible patient informations were collected and reported to qualified assessor/s before visiting clinical areas, confirming delirium presence and undertaking DRS- R98 assessments. To assess the tool's construct validity, an intensivist completed the Clinical Global Impression-Scale (CGI-S). To calculate the inter-rater reliability (IRR) a subset of patients were simultaneously evaluated by two assessors.
Results: We assessed 22 patients, 73% were male, with a median age of 65 years (IQR14). The DRS -R98 mean (SD) severity score was 24 (+/-7.7), total scale was 29 (+/18.0), and CGI-S 3.5 (+/11.5). Assessment duration was 90 min (+/-55) and 15 min (+/-5) for record data extraction and clinical assessment respectively. The CGI-S significantly correlated with DRS-R98 severity (r = 0.626) and total (r = 0.628) scales. The DRS-R98 Cronbach's alpha was 0.896 for severity scale and 0.886 for total scale. The inter-rater reliability (IRR) was assessed in six patients and reported an inter-correlation coefficient of 0.505 (p = 0.124) and 0.565 (p = 0.93) for the severity and total scale respectively.
Conclusions: In critical care, the Delirium Rating Scale R98 had good construct validity, excellent internal consistency, and moderate inter-rater reliability.
Keywords: critical care; delirium; intensive care; severity; validation.
Figures
References
-
- Ely EW, Girard TD, Shintani AK, et al. Apolipoprotein E4 polymorphism as a genetic predisposition to delirium in critically ill patients. Crit Care Med. 2007;35(1):112-117. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical