Validity and reliability of the adapted Dutch version of the Brace Questionnaire (BrQ)
- PMID: 37670558
- PMCID: PMC10481702
- DOI: 10.2340/17453674.2023.18492
Validity and reliability of the adapted Dutch version of the Brace Questionnaire (BrQ)
Abstract
Background and purpose: The Brace Questionnaire (BrQ) is a disease-specific health-related quality of life (HRQOL) instrument for measuring perceived health status of scoliosis patients undergoing brace treatment. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the validity and reliability of a translated and culturally adapted Dutch version of the BrQ.
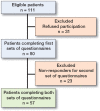
Patients and methods: The original Greek BrQ was translated into Dutch and a cross-cultural adaptation and validation processes were conducted. Subsequently, 80 adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS) patients undergoing active brace treatment were included from 4 scoliosis centers to evaluate the validity and reliability of the Dutch version of the BrQ. The questionnaire's floor and ceiling effects, internal consistency, and test-retest reliability were assessed. Concurrent validity was evaluated by comparing the BrQ with the revised Scoliosis Research Society 22-item questionnaire (SRS-22r) scores.
Results: The mean total BrQ score was 75.9 (standard deviation [SD] 11.3) and the mean domain scores varied between 3.4 (SD 0.9) and 4.2 (SD 0.7) for the domains "vitality" and "bodily pain," respectively. There were no floor and ceiling effects for the total BrQ score. The BrQ showed satisfactory internal consistency in most subdomains with a Cronbach's α ranging between 0.35 for the domain "general health perception" and 0.89 for the domain "self-esteem and aesthetics." Excellent test-retest reproducibility was observed for the total BrQ score (ICC 0.91), and the BrQ was successfully validated against the SRS-22r.
Conclusion: The translated and culturally adapted Dutch version of the BrQ is a valid and reliable HRQOL instrument for AIS patients undergoing brace treatment.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical