Sitosterol-rich Digera muricata against 7-ketocholesterol and lipopolysaccharide-mediated atherogenic responses by modulating NF-ΚB/iNOS signalling pathway in macrophages
- PMID: 37670802
- PMCID: PMC10475456
- DOI: 10.1007/s13205-023-03741-6
Sitosterol-rich Digera muricata against 7-ketocholesterol and lipopolysaccharide-mediated atherogenic responses by modulating NF-ΚB/iNOS signalling pathway in macrophages
Abstract
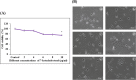
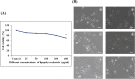
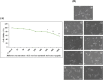
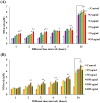
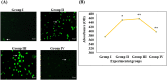
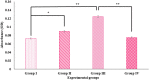
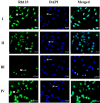
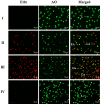
Digera muricata L., commonly known as Tartara, is an edible herb used as traditional medicine in many countries of Africa and Asia. This study aimed to elucidate the effect of a phytosterol-rich extract of D. muricata on 7-ketocholesterol-mediated atherosclerosis in macrophages. The extract was examined by phytochemical analyses, GC-MS, TLC, DPPH scavenging and hRBC membrane stabilization assays. Macrophage polarization was studied with experimental groups framed based on alamar blue cell viability and griess assays. Regulations of arginase enzyme activity, ROS generation, mitochondrial membrane potential, cell membrane integrity, pinocytosis, lipid uptake and peroxidation, as well as, intracellular calcium deposition were determined. In addition, expressions of atherogenic mediators were analysed using PCR, ELISA and immunocytochemistry techniques. Diverse phytochemicals with higher free radical scavenging activity and anti-inflammatory potential have been detected in the D. muricata. Co-treatment with D. muricata markedly reduced the atherogenic responses induced by 7KCh in the presence of LPS such as ROS, especially, NO and O2- along with lipid peroxidation. Furthermore, D. muricata significantly normalized mitochondrial membrane potential, cell membrane integrity, pinocytic activity, intracellular lipid accumulation and calcium deposition. These results provided us with the potentiality of D. muricata in ameliorating atherogenesis. Additionally, it decreased the expression of pro-atherogenic mediators (iNOS, COX-2, MMP9, IL-6, IL-1β, CD36, CD163 and TGFβ1) and increased anti-atherogenic mediators (MRC1 and PPARγ) with high cellular expressions of NF-κB and iNOS. Results showed the potential of sitosterol-rich D. muricata as a versatile biomedical therapeutic agent against abnormal macrophage polarization and its associated pathologies.
Keywords: 7-ketocholesterol; Atherosclerosis; Cytokines; Macrophages; Phytosterol.
© King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest in the publication.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Phytol from Scoparia dulcis prevents NF-κB-mediated inflammatory responses during macrophage polarization.3 Biotech. 2024 Mar;14(3):80. doi: 10.1007/s13205-024-03924-9. Epub 2024 Feb 17. 3 Biotech. 2024. PMID: 38375513 Free PMC article.
-
Pinocembrin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in Labeo rohita macrophages via the suppression of the NF-κB signalling pathway.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016 Sep;56:459-466. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2016.07.038. Epub 2016 Aug 2. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27492123
-
[Zhuyu Pills promote polarization of macrophages toward M2 phenotype to prevent atherosclerosis via PPARγ/NF-κB signaling pathway].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2024 Jan;49(1):243-250. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20230823.501. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38403357 Chinese.
-
Flavonoid fraction of guava leaf extract attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response via blocking of NF-κB signalling pathway in Labeo rohita macrophages.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015 Nov;47(1):85-92. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2015.08.031. Epub 2015 Aug 29. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26327113
-
[Study on the anti-sepsis mechanism of ursolic acid by targeting myeloid differentiation protein-2].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2023 May;35(5):476-481. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20220705-00634. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2023. PMID: 37308226 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Oxysterol-Induced Inflammation in Human Diseases: Strategies for Treatment with Natural Compounds and Synthetic Molecules.Molecules. 2025 Jul 7;30(13):2883. doi: 10.3390/molecules30132883. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40649397 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phytol from Scoparia dulcis prevents NF-κB-mediated inflammatory responses during macrophage polarization.3 Biotech. 2024 Mar;14(3):80. doi: 10.1007/s13205-024-03924-9. Epub 2024 Feb 17. 3 Biotech. 2024. PMID: 38375513 Free PMC article.
-
Fenchone attenuates CD68-dependent 7-ketocholesterol accumulation, cholesterol dyshomeostasis and inflammatory responses via modulation of macrophage polarization.Inflammopharmacology. 2025 Jul 1. doi: 10.1007/s10787-025-01836-5. Online ahead of print. Inflammopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 40591211
References
-
- Adegbola PI, Adetutu A, et al. Antioxidant activity of Amaranthus species from the Amaranthaceae family—a review. S Afr J Bot. 2020;1(133):111–117. doi: 10.1016/j.sajb.2020.07.003. - DOI
-
- Afrin S, Gasparrini M, et al. Protective effects of Manuka honey on LPS-treated RAW 264.7 macrophages. Part 1: enhancement of cellular viability, regulation of cellular apoptosis and improvement of mitochondrial functionality. Food Chem Toxicol. 2018;1(121):203–213. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2018.09.001. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arulmathi R, Sudarmani DN, et al. Screening and evaluation of invasive weeds against Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Mtcc 3541) for quorum sensing interference and its free radical scavenging. Res J Pharm Technol. 2017;10(2):525–528. doi: 10.5958/0974-360X.2017.00104.4. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

