The effect of Iran's health sector evolution plan on hospitals performance indicators: an interrupted time series analysis
- PMID: 37670895
- PMCID: PMC10475734
- DOI: 10.3389/frhs.2023.1144685
The effect of Iran's health sector evolution plan on hospitals performance indicators: an interrupted time series analysis
Abstract
Background: The Health Sector Evolution Plan (HSEP) was set up in Iran's health system to respond to some of the main problems in hospitals and other health sectors. We aimed to compare the effect of the HSEP on teaching hospital performance before and after the implementation of the HSEP through the interrupted time series (ITS) analysis.
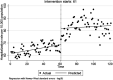
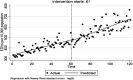
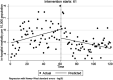
Methods: With a cross-sectional design, data collection was performed in 17 teaching hospitals affiliated with the Kermanshah University of Medical Sciences (KUMS). We used the existing data on three indicators of hospitalization rate (per 10,000 population), Emergency Department Visits (EDVs) (per 10,000 population), and in-hospital mortality (per 10,000 population). The monthly data from 2009 to 2019 was analyzed by the ITS method 60 months before and 61 months after the HSEP.
Results: We found a non-statistically significant decrease in the monthly trend of hospitalization rate relative to the period before the HSEP implementation (-0.084 per 10,000 population [95%CI: -0.269, 0.101](. There was a statistically significant increase in the monthly trend of EDVs rate compared to before the HSEP implementation (1.07 per 10,000 population [95%CI: 0.14, 2.01]). Also, a significant decrease in the monthly trend of in-hospital mortality compared to before the HSEP implementation [-0.003 per 10,000 population (95%CI: -0.006, -0.001)] was observed.
Conclusion: Our study demonstrated a significant increasing and decreasing trend for EDVs and in-hospital mortality following the HSEP implementation, respectively. Regarding the increase in hospitalization rate and EDVs after the implementation of HESP, it seems that there is a need to increase investment in healthcare and improve healthcare infrastructure, human resources-related indicators, and the quality of healthcare.
Keywords: Iran; health sector evolution plan; hospital; hospitalization; interrupted time series.
© 2023 Soltani, Rezaei, Kazemi-Karyani, Azimi, Jalili, Roshani, Najafi, Bagheri and Salimi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The impact of health sector evolution plan on hospitalization and cesarean section rates in Iran: an interrupted time series analysis.Int J Qual Health Care. 2018 Feb 1;30(1):75-79. doi: 10.1093/intqhc/mzx169. Int J Qual Health Care. 2018. PMID: 29272503
-
Hospitalization costs and out-of-pocket (OOP) payment in lung cancer patients in Iran: Health Sector Evolution Plan (HSEP) has reduced OOP payments and improved financial protection.PLoS One. 2024 Dec 19;19(12):e0297934. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0297934. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39700126 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the performance of hospitals before and after the implementation of Iran's Health Sector Evolution Plan (HSEP) using the Pabon Lasso model.Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2021 Feb 15;35:23. doi: 10.47176/mjiri.35.23. eCollection 2021. Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2021. PMID: 34169035 Free PMC article.
-
Inappropriate Rate of Admission and Hospitalization in the Iranian Hospitals: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Value Health Reg Issues. 2020 May;21:105-112. doi: 10.1016/j.vhri.2019.07.011. Epub 2019 Nov 5. Value Health Reg Issues. 2020. PMID: 31704488
-
Efficiency of Iranian Hospitals Before and After Health Sector Evolution Plan: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Study.Front Public Health. 2021 Nov 25;9:727669. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.727669. eCollection 2021. Front Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34900889 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on governmental hospitals performance indicators in city of Yazd, Iran: an interrupted time-series analysis.BMC Health Serv Res. 2025 Mar 26;25(1):438. doi: 10.1186/s12913-025-12587-y. BMC Health Serv Res. 2025. PMID: 40140858 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing Hospital Services: Achieving High Quality Under Resource Constraints.Health Serv Insights. 2025 Apr 11;18:11786329251331311. doi: 10.1177/11786329251331311. eCollection 2025. Health Serv Insights. 2025. PMID: 40290849 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges and Weaknesses of Leadership and Governance-related Health Policies in Iran: A Systematic Review.Arch Iran Med. 2024 Sep 1;27(9):508-521. doi: 10.34172/aim.28907. Epub 2024 Sep 1. Arch Iran Med. 2024. PMID: 39465526 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hashemi N, Farhani Nezhad S, Faghih A, Imani E, Nazari F, Kashani S. Evaluation of inpatient satisfaction from the implementation of the health system evolution program (HSEP). J Prevent Med. (2017) 4(2):32–9.
-
- Shamsaei M, Shamsaei M, Mohammadnezhad S, Bahlgardi R, Isfahani P. Comparison of hospital indicators before and after the implementation of the health sector evaluation plan in teaching hospitals of Zabol University of Medical Sciences (Iran).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources