Detection of Inflammatory Biomarkers Among Patients with Sepsis of Gram-Negative Bacteria: A Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 37670930
- PMCID: PMC10476660
- DOI: 10.2147/IJGM.S415200
Detection of Inflammatory Biomarkers Among Patients with Sepsis of Gram-Negative Bacteria: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
Background: Sepsis is a highly mixed ailment that affects patients with numerous conditions of infectious sources and can lead to multi-organ failure with dysregulated host immune response.
Objective: To determine inflammatory biomarkers in patients with sepsis caused by Gram-negative bacteria and compare their role in the early detection of sepsis.
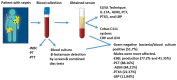
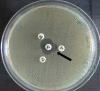
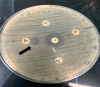
Methods: This cross-sectional study was conducted on patients with sepsis admitted to the intensive care unit at different hospitals in Sulaimaniyah, Iraq, from May to December 2021. Patients (n=147) were enrolled in this study according to the primary diagnosis of sepsis by Sequential Organ Failure Assessment scores. Blood samples were taken from patients to investigate white blood cells, inflammatory biomarkers (pentraxin-3, procalcitonin, adrenomedullin, lipopolysaccharide binding protein, interleukin-17A, lactate dehydrogenase, and C-creative protein), blood culture, antibiotic susceptibility test, and coagulation biomarkers (Prothrombin time, activated partial thromboplastin time, and international normalized ratio). Then, isolated Gram-negative bacteria were tested for extended-spectrum β-lactamase enzymes production by screening and combined disc tests.
Results: A total of 51.7% samples were blood culture positive for different Gram-negative bacteria, and P. aeruginosa (51.95%) was a more isolated bacterium. Both males and females were affected by sepsis in a ratio of 1.23:1 with different age groups. Extended-spectrum β-lactamase was estimated to be 77.2% by antibiotic profile, and the rate decreased using two double-disc synergy tests. This was confirmed by combined disc test at a rate of 41.35%. The most prevalent biomarkers were procalcitonin (88.16%), adrenomedullin (84.21%), pentraxin-3 (22.37%), and lipopolysaccharide binding protein (11.84%).
Conclusion: Sepsis is a life-threatening condition that can be diagnosed early by several blood biomarkers such as procalcitonin, adrenomedullin, and pentraxin-3 combined with a standard blood culture technique to improve the patient outcome.
Keywords: Gram-negative bacteria; SOFA score; double-disc synergy test; sepsis biomarkers; β-Lactamase.
© 2023 Khana and Anwar.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
High burden of ESBL and carbapenemase-producing gram-negative bacteria in bloodstream infection patients at a tertiary care hospital in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.PLoS One. 2023 Jun 27;18(6):e0287453. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0287453. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37368908 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of novel biomarkers: sTREM-1, pentraxin-3 and pro-adrenomedullin in the early diagnosis of neonatal early onset sepsis.J Neonatal Perinatal Med. 2020;13(1):47-54. doi: 10.3233/NPM-180131. J Neonatal Perinatal Med. 2020. PMID: 31594258
-
Pentraxin 3 (PTX3) as a Predictor of Severity of Sepsis in Patients Admitted to an Intensive Care Unit: A Cross-Sectional Study From North India.Cureus. 2022 Aug 22;14(8):e28282. doi: 10.7759/cureus.28282. eCollection 2022 Aug. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36168379 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive performance of critical illness scores and procalcitonin in sepsis caused by different gram-stain bacteria.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2021 Jun 11;76:e2610. doi: 10.6061/clinics/2021/e2610. eCollection 2021. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2021. PMID: 34133658 Free PMC article.
-
The efficacy of procalcitonin as a biomarker in the management of sepsis: slaying dragons or tilting at windmills?Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2013 Dec;14(6):489-511. doi: 10.1089/sur.2012.028. Epub 2013 Nov 25. Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2013. PMID: 24274059 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of Clinical Characteristics and Biomarkers in Culture-Positive and Culture-Negative Sepsis Patients.Cureus. 2024 Apr 21;16(4):e58682. doi: 10.7759/cureus.58682. eCollection 2024 Apr. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38774176 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 levels on pathogenic bacteria types in patients with advanced lung cancer and pulmonary infection during chemotherapy.Am J Transl Res. 2025 Jun 15;17(6):4723-4732. doi: 10.62347/GRGQ7128. eCollection 2025. Am J Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 40672607 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmad S, Ismaeel SM, Mohammed DA, et al. Outcome and management of sepsis at Rozhhalat emergency hospital in Erbil –Kurdistan region of Iraq. J Appl Res. 2018;2018:21–30.
-
- Hung Y-L, Suzuki K. The pattern recognition receptors and lipopolysaccharides (LPS)-induced systemic inflammation. Int J Med Sci Public Health. 2017;2(7):1–7.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

