Manufacture of titanium alloy materials with bioactive sandblasted surfaces and evaluation of osseointegration properties
- PMID: 37671189
- PMCID: PMC10475539
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1251947
Manufacture of titanium alloy materials with bioactive sandblasted surfaces and evaluation of osseointegration properties
Abstract
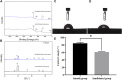
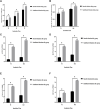
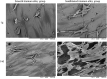
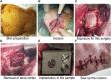
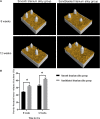
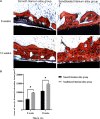
Titanium alloys are some of the most important orthopedic implant materials currently available. However, their lack of bioactivity and osteoinductivity limits their osseointegration properties, resulting in suboptimal osseointegration between titanium alloy materials and bone interfaces. In this study, we used a novel sandblasting surface modification process to manufacture titanium alloy materials with bioactive sandblasted surfaces and systematically characterized their surface morphology and physicochemical properties. We also analyzed and evaluated the osseointegration between titanium alloy materials with bioactive sandblasted surfaces and bone interfaces by in vitro experiments with co-culture of osteoblasts and in vivo experiments with a rabbit model. In our in vitro experiments, the proliferation, differentiation, and mineralization of the osteoblasts on the surfaces of the materials with bioactive sandblasted surfaces were better than those in the control group. In addition, our in vivo experiments showed that the titanium alloy materials with bioactive sandblasted surfaces were able to promote the growth of trabecular bone on their surfaces compared to controls. These results indicate that the novel titanium alloy material with bioactive sandblasted surface has satisfactory bioactivity and osteoinductivity and exhibit good osseointegration properties, resulting in improved osseointegration between the material and bone interface. This work lays a foundation for subsequent clinical application research into titanium alloy materials with bioactive sandblasted surfaces.
Keywords: bioactive sandblasted surface; biomaterial; osseointegration; surface modification; titanium alloy.
Copyright © 2023 Wang, Yang, Guo, Yu and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

