Amiodarone-induced syndrome of inappropriate antidiuresis with hepatic transaminitis
- PMID: 37671261
- PMCID: PMC10477045
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jccase.2023.05.004
Amiodarone-induced syndrome of inappropriate antidiuresis with hepatic transaminitis
Abstract
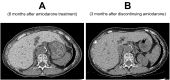
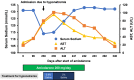
A 72-year-old woman with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy was admitted to the hospital after an appropriate implantable cardioverter-defibrillator shock for ventricular fibrillation. She was discharged after the addition of amiodarone. Eight months after discharge, she was admitted to the hospital with a sign of somnolence. She had low levels of serum sodium and plasma osmolality, as well as hepatic transaminitis. She underwent a computed tomography scan, which detected high liver density. Amiodarone-induced syndrome of inappropriate antidiuresis with hepatic transaminitis was diagnosed, and amiodarone was discontinued. After discharge, her hepatic transaminitis improved, and there was no recurrence of hyponatremia with a sign of somnolence. Amiodarone is an important drug used to treat ventricular arrhythmias. However, it has a variety of adverse effects. Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuresis is a rare complication of amiodarone. If hyponatremia occurs after starting amiodarone, this complication should be considered.
Learning objective: Amiodarone is an important drug used to treat ventricular arrhythmias, such as ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation. However, amiodarone has a variety of adverse effects. Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuresis is a rare complication of amiodarone. If hyponatremia occurs after starting amiodarone, this complication should be considered.
Keywords: Adverse effects; Amiodarone; Hyponatremia.
© 2023 Japanese College of Cardiology. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kim B.-B., Kim D.-M., Choi D.-H., Chung J.-W., Koh Y.-Y., Chang K.-S., Hong S.P. Amiodarone toxicity showing high liver density on CT scan with normal liver function and plasma amiodarone levels in a long-term amiodarone user. Int J Cardiol. 2014;172:494–495. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2014.01.020. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tsuda T., Tada H., Tanaka Y., Nishida N., Yoshida T., Sawada T., Sakata K., Hayashi K., Kawashiri M.A., Oyama T., Sasaki M., Kurose N., Yamagishi M. Amiodarone-induced reversible and irreversible hepatotoxicity: two case reports. J Med Case Rep. 2018;12:95. doi: 10.1186/s13256-018-1629-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources