Physiological Mechanisms of Dietary Salt Sensing in the Brain, Kidney, and Gastrointestinal Tract
- PMID: 37671571
- PMCID: PMC10915107
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.123.19488
Physiological Mechanisms of Dietary Salt Sensing in the Brain, Kidney, and Gastrointestinal Tract
Abstract
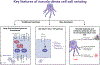
Excess dietary salt (NaCl) intake is strongly correlated with cardiovascular disease and is a major contributing factor to the pathogenesis of hypertension. NaCl-sensitive hypertension is a multisystem disorder that involves renal dysfunction, vascular abnormalities, and neurogenically-mediated increases in peripheral resistance. Despite a major research focus on organ systems and these effector mechanisms causing NaCl-induced increases in arterial blood pressure, relatively less research has been directed at elucidating how NaCl is sensed by various tissues to elicit these downstream effects. The purpose of this review is to discuss how the brain, kidney, and gastrointestinal tract sense NaCl including key cell types, the role of NaCl versus osmolality, and the underlying molecular and electrochemical mechanisms.
Keywords: NaCl; angiotensin II; cardiovascular diseases; renal; sodium.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Appel LJ, Frohlich ED, Hall JE, Pearson TA, Sacco RL, Seals DR, Sacks FM, Smith SC Jr., Vafiadis DK, Van Horn LV. The importance of population-wide sodium reduction as a means to prevent cardiovascular disease and stroke: a call to action from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2011;123:1138–1143. doi: CIR.0b013e31820d0793 [pii]10.1161/CIR.0b013e31820d0793 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Whelton PK, Appel LJ, Sacco RL, Anderson CA, Antman EM, Campbell N, Dunbar SB, Frohlich ED, Hall JE, Jessup M, et al. Sodium, blood pressure, and cardiovascular disease: further evidence supporting the American Heart Association sodium reduction recommendations. Circulation. 2012;126:2880–2889. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0b013e318279acbf - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

