Prediction of Fuhrman nuclear grade for clear cell renal carcinoma by a multi-information fusion model that incorporates CT-based features of tumor and serum tumor associated material
- PMID: 37672076
- PMCID: PMC11798235
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-023-05353-2
Prediction of Fuhrman nuclear grade for clear cell renal carcinoma by a multi-information fusion model that incorporates CT-based features of tumor and serum tumor associated material
Abstract
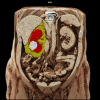
Purpose: Prediction of Fuhrman nuclear grade is crucial for making informed herapeutic decisions in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC). The current study aimed to develop a multi-information fusion model utilizing computed tomography (CT)-based features of tumors and preoperative biochemical parameters to predict the Fuhrman nuclear grade of ccRCC in a non-invasive manner.
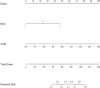
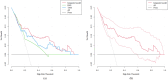
Methods: 218 ccRCC patients confirmed by histopathology were retrospectively analyzed. Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses were performed to identify independent predictors and establish a model for predicting the Fuhrman grade in ccRCC. The predictive performance of the model was evaluated using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves, calibration, the 10-fold cross-validation method, bootstrapping, the Hosmer-Lemeshow test, and decision curve analysis (DCA).
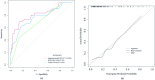
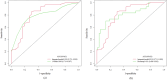
Results: R.E.N.A.L. Nephrometry Score (RNS) and serum tumor associated material (TAM) were identified as independent predictors for Fuhrman grade of ccRCC through multivariate logistic regression. The areas under the ROC curve (AUC) for the multi-information fusion model composed of the above two factors was 0.810, higher than that of the RNS (AUC 0.694) or TAM (AUC 0.764) alone. The calibration curve and Hosmer-Lemeshow test showed the integrated model had a good fitting degree. The 10-fold cross-validation method (AUC 0.806) and bootstrap test (AUC 0.811) showed the good stability of the model. DCA demonstrated that the model had superior clinical utility.
Conclusion: A multi-information fusion model based on CT features of tumor and routine biochemical indicators, can predict the Fuhrman grade of ccRCC using a non-invasive approach. This model holds promise for assisting clinicians in devising personalized management strategies.
Keywords: Clear cell renal cell carcinoma; Computed tomography; Fuhrman grade; Predict.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Predictive value of CT-based tumor and peritumoral radiomics for WHO/ISUP grading of non-metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2025 Jul 15;105(26):2195-2202. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20250226-00460. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40660974 Chinese.
-
A predictive model for WHO/ISUP pathologic grading of renal clear cell carcinoma based on CT radiomics: a multicenter study.BMC Nephrol. 2025 Jul 1;26(1):296. doi: 10.1186/s12882-025-04268-z. BMC Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40597030 Free PMC article.
-
Computed tomography-based radiomics predicts prognostic and treatment-related levels of immune infiltration in the immune microenvironment of clear cell renal cell carcinoma.BMC Med Imaging. 2025 Jul 1;25(1):213. doi: 10.1186/s12880-025-01749-3. BMC Med Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40596969 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
-
A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis Comparing the Effectiveness and Adverse Effects of Different Systemic Treatments for Non-clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma.Eur Urol. 2017 Mar;71(3):426-436. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.11.020. Epub 2016 Dec 8. Eur Urol. 2017. PMID: 27939075
Cited by
-
CT Urography-Based Radiomics to Predict ISUP Grading of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma.J Cancer. 2025 Jan 6;16(4):1118-1126. doi: 10.7150/jca.105173. eCollection 2025. J Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39895776 Free PMC article.
-
Deep learning using contrast-enhanced ultrasound images to predict the nuclear grade of clear cell renal cell carcinoma.World J Urol. 2024 Mar 21;42(1):184. doi: 10.1007/s00345-024-04889-3. World J Urol. 2024. PMID: 38512539
-
Association between CT-based adipose variables, preoperative blood biochemical indicators and pathological T stage of clear cell renal cell carcinoma.Heliyon. 2024 Jan 13;10(2):e24456. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24456. eCollection 2024 Jan 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38268833 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Camacho JC, Kokabi N, Xing M et al (2015) R.E.N.A.L. (radius, exophytic/endophytic, nearness to collecting system or sinus, anterior/posterior, and location relative to polar lines) nephrometry score predicts early tumor recurrence and complications after percutaneous ablative therapies for renal cell carcinoma: a 5-year experience. J Vasc Interv Radiol 26(5):686–693. 10.1016/j.jvir.2015.01.008 - PubMed
-
- Chang TW, Cheng WM, Fan YH et al (2021) Predictive factors for disease recurrence in patients with locally advanced renal cell carcinoma treated with curative surgery. J Chin Med Assoc 84(4):405–409. 10.1097/JCMA.0000000000000501 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

