Conjugation of microbial-derived gold nanoparticles to different types of nucleic acids: evaluation of transfection efficiency
- PMID: 37674013
- PMCID: PMC10482973
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-41567-7
Conjugation of microbial-derived gold nanoparticles to different types of nucleic acids: evaluation of transfection efficiency
Abstract
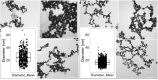
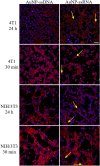
In this study, gold nanoparticles produced by eukaryotic cell waste (AuNP), were analyzed as a transfection tool. AuNP were produced by Fusarium oxysporum and analyzed by spectrophotometry, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS). Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and dynamic light scattering (DLS) were used before and after conjugation with different nucleic acid (NA) types. Graphite furnace atomic absorption spectroscopy (GF-AAS) was used to determine the AuNP concentration. Conjugation was detected by electrophoresis. Confocal microscopy and quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) were used to assess transfection. TEM, SEM, and EDS showed 25 nm AuNP with round shape. The amount of AuNP was 3.75 ± 0.2 µg/µL and FTIR proved conjugation of all NA types to AuNP. All the samples had a negative charge of - 36 to - 46 mV. Confocal microscopy confirmed internalization of the ssRNA-AuNP into eukaryotic cells and qPCR confirmed release and activity of carried RNA.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Pourali P, et al. Biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles by two bacterial and fungal strains, Bacillus cereus and Fusarium oxysporum, and assessment and comparison of their nanotoxicity in vitro by direct and indirect assays. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2017;29:86–93. doi: 10.1016/j.ejbt.2017.07.005. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

